Figure EV2. Binding of the SIR complex to highly expressed genomic loci mediates camptothecin sensitivity.
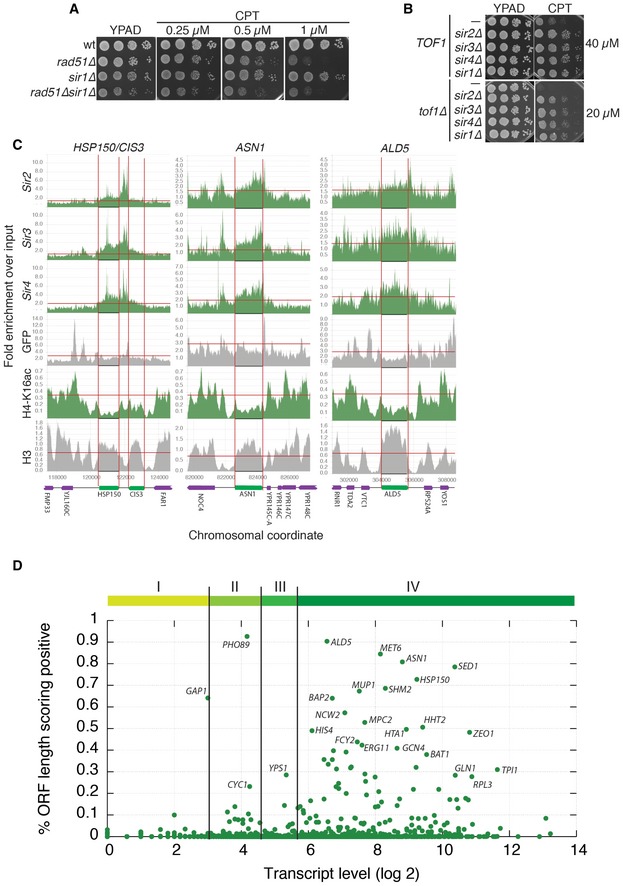
- Deletion of SIR1 does not rescue camptothecin hypersensitivity in rad51∆ cells.
- Deletion of SIR1, SIR2, SIR3 or SIR4 increases camptothecin resistance to a similar extent, both in a wild‐type and in a tof1∆ background.
- Analysis of ChIP‐seq data for the indicated proteins: enrichment is plotted as a function of the genomic coordinate; in green is the protein/modification tested; in grey are controls. The position of each ORF is indicated at the bottom of the panel and by two vertical red lines. The horizontal red lines indicate the thresholds used in this work to determine enrichment (Sir2/Sir3/Sir4/GFP/H3) or loss (H4‐K16) of ChIP signal.
- The majority of SIR‐positive ORFs are highly expressed genes, but high expression does not necessarily correlate with high SIR score. Vertical lines identify quartiles (I, II, III, IV) of the gene expression distribution.
