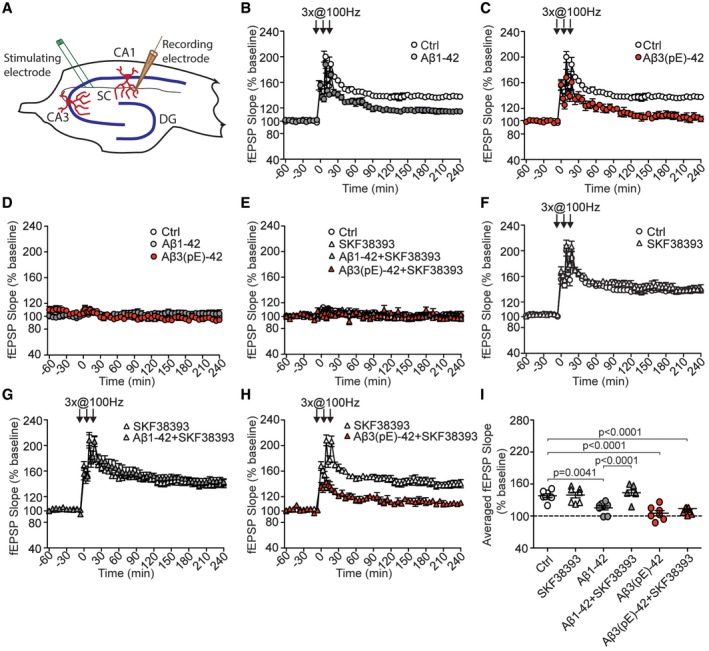
Figure 3. An agonist of dopamine D1/D5 receptors selectively rescues late LTP impaired by Aβ1‐42, but not Aβ3(pE)‐42.
-
A–C(A) Schematic representation of electrode positioning in acute hippocampal slice. LTP recordings revealed that both (B) Aβ1‐42 (n = 8) and (C) Aβ3(pE)‐42 (n = 7) cause impairment of late phase LTP compared to control measurements (n = 8).
-
DBasal synaptic transmission is not affected by bath application of Aβ1‐42 (n = 8) or Aβ3(pE)‐42 (n = 7) oligomers.
-
EBasal synaptic transmission is not affected by dopamine D1/D5 receptor agonist SKF38393 (n = 7) applied alone or together with Aβ oligomers (n = 7 in each group).
-
FApplication of SKF38393 in control conditions does not alter tetanisation‐triggered LTP.
-
G, HActivation of D1/D5 receptors by SKF38393 restores the CA1 LTP in Aβ1‐42‐treated (n = 7), but not Aβ3(pE)‐42‐treated slices (n = 7).
-
IDot plot representing averaged fEPSP slope. P‐values versus control by one‐way ANOVA.
