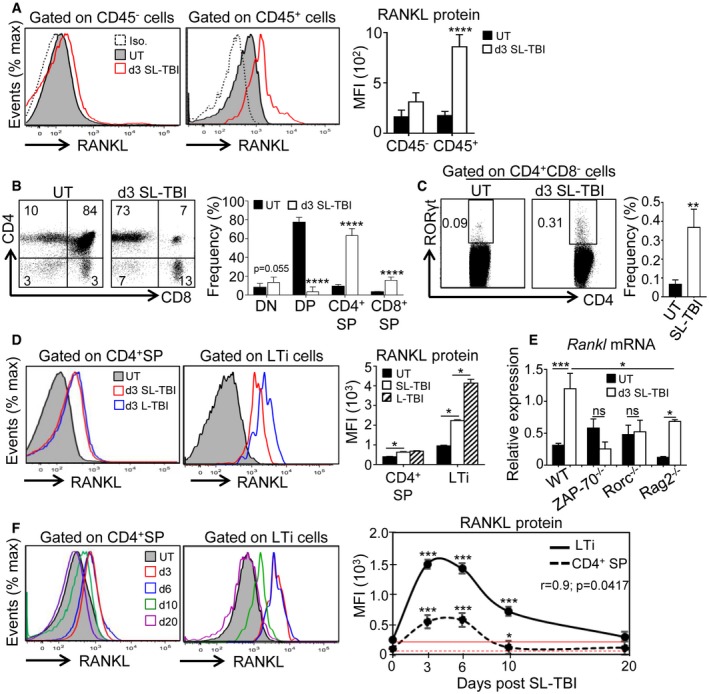
Figure 1. RANKL is upregulated in CD4+ SP and LTi cells during the course of thymic regeneration.
-
AExpression of RANKL protein analyzed by flow cytometry in CD45− and CD45+ thymic cells from untreated (UT) WT mice or at d3 SL‐TBI.
-
B, CFlow cytometry profiles and frequencies of DN (double negative), DP (double positive), CD4+ and CD8+ SP (single positive) (B), and LTi cells (C) from untreated (UT) WT mice or at d3 SL‐TBI.
-
DExpression level of RANKL protein in CD4+ SP and LTi cells from UT WT mice or at d3 SL‐TBI and L‐TBI.
-
EExpression of Rankl mRNA in the total thymus isolated from UT WT, Rorc−/−, ZAP‐70−/−, and Rag2−/− mice or at d3 SL‐TBI (n = 3–6 mice per genotype).
-
FCD4+ SP and LTi cells from UT WT mice or at d3, d6, d10, and d20 SL‐TBI with no hematopoietic rescue were analyzed for the expression of RANKL protein. Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of RANKL in CD4+ SP and LTi cells over time following SL‐TBI. The red lines represent the MFI of RANKL at baseline.
