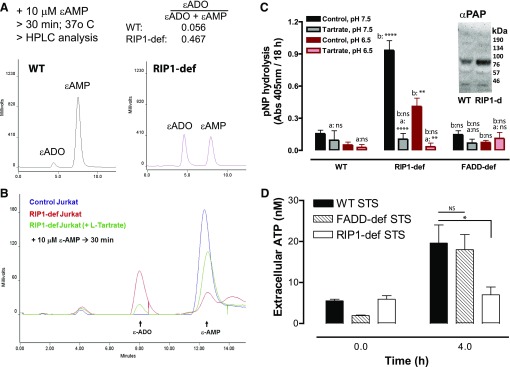
Fig. 8.
Increased ecto-AMPase activity in RIP1-deficient Jurkat cells correlates with up-regulation of PAP. (A) 10 μM ε-AMP was added to WT or RIP1-deficient cells (2 × 106 cells/ml). Cell-free supernatants were collected after 30 minutes and processed for separation and quantification of ε-ADO and ε-AMP by anion exchange HPLC and fluorescence detection. Data are representative of three experiments. (B) We added 10 μM ε-AMP to WT or RIP1-deficient cells (2 × 106 cells/ml) in the absence or presence of 10 mM l-tartrate. Cell-free supernatants were collected after 30 minutes and processed for separation and quantification of ε-ADO and ε-AMP by anion exchange HPLC and fluorescence detection. Data are representative of four experiments. (C) WT, RIP1-deficient, or FADD-deficient Jurkat cells (2 × 106/ml) were plated in 96-well plates and suspended in BSS that was buffered to pH 7.5 or pH 6.5. The cell suspensions were supplemented with 500 μM p-nitrophenyl phosphate in the absence or presence of 10 mM l-tartrate and incubated for 18 hours at 25°C. Hydrolysis of nitrophenyl phosphate to nitrophenyl was assayed by measuring absorbance at 405 mm. Data indicate mean ±S.E. of three independent experiments. Analysis by two-way analysis of variance and Tukey post-test comparison; a: +tartrate versus −tartrate; b:RIP1-def or FADD-def versus WT. (C, inset) Western blot analysis of PAP expression in whole-cell lysates from WT or RIP1-deficient Jurkat cells that were resolved by SDS-PAGE and transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride membranes; mobility of molecular mass markers is indicated on the right. (D) WT, FADD-deficient, and RIP1-deficient Jurkat cells were treated with 3 μM STS for 4 hours. Extracellular media samples were collected and assayed for extracellular ATP. Data indicate mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments. Analysis by two-way analysis of variance and Tukey post-test comparison. All panels: ns, not statistically significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001.