Table 3. Further optimization of C(sp2)–H hydroxylation a , b .
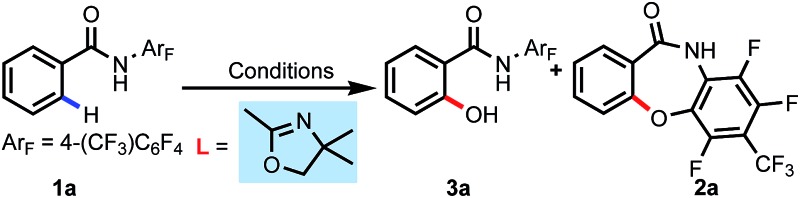
| |||||
| Entry | Copper salts | Base | Acid | Yield |
|
| 3a | 2a | ||||
| 1 | Cu(OAc)2 + CuBr | Cs2CO3 | PivOH | 59 | 12 |
| 2 | Cu(OAc)2 + CuBr | Cs2CO3 | 1-Ad-COOH | 61 | 13 |
| 3 c | Cu(OAc)2 + CuBr | Cs2CO3 | 1-Ad-COOH | 63 | 12 |
| 4 c , d | Cu(OAc)2 + CuBr | Cs2CO3 | 1-Ad-COOH | 63 | 11 |
| 5 c , d , e | Cu(OAc)2 + CuBr | Cs2CO3 | 1-Ad-COOH | 66 | 8 |
| 6 c , d , e , f | Cu(OAc)2 + CuBr | Cs2CO3 | 1-Ad-COOH | 67 | 8 |
| 7 c , d , e , f | Cu(OPiv) 2 + CuBr | Cs 2 CO 3 | 1-Ad-COOH | 75(80) g | 0 |
| 8 c , d , e , f | Cu(OCOiPr)2 + CuBr | Cs2CO3 | 1-Ad-COOH | 68 | 0 |
| 9 c , d , e , f | Cu(OCO)2 + CuBr | Cs2CO3 | 1-Ad-COOH | 45 | 0 |
aReaction conditions: 1 (0.1 mmol), Cu(OAc)2 (0.2 mmol), CuBr (0.08 mmol), base (0.15 mmol), acid (0.15 mmol), ligand (0.1 mmol), DMSO (1.0 mL), 100 °C, air, 6 h.
bYield determined by 1H NMR analysis of crude reaction mixture using CH2Br2 as an internal standard.
cAcid (0.18 mmol).
dCuX2 (0.15 mmol).
eDMSO (0.5 mL).
fLigand (0.04 mmol).
g105 °C.
