Table 1. Au(i)-catalyzed C–O bond formation with different NaO–R a .
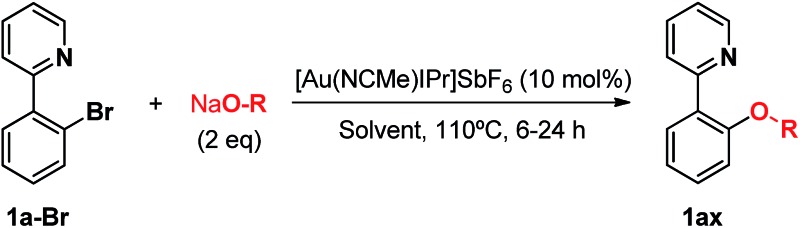
| |||||
| Entry | R–ONa | Solvent | Time (h) | Product | Yield b (%) |
| 1 | pCl-PhONa | CH3CN | 6 |
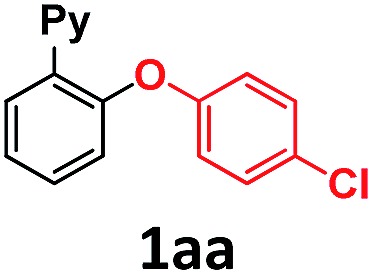
|
>99 c |
| 2 | HONa | MeOH | 8 |
|
>99 |
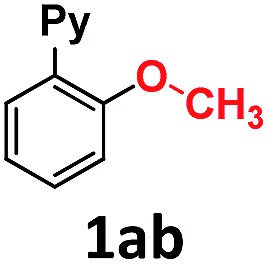
| 3 | MeONa | MeOH | 8 | >99 c | |
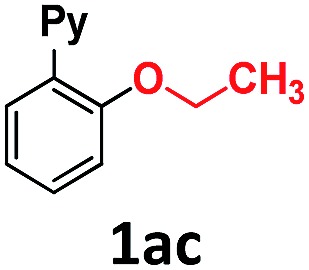
| 4 | EtONa | MeOH | 24 | >99 | |
| 5 | MeONa | EtOH | 24 | 86 (9) d | |
| 6 | EtONa | EtOH | 24 |
|
56 (78) e |
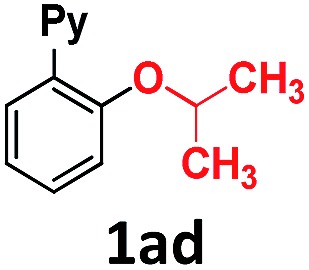
| 7 | (2-Propoxide)Na f | 2-Propanol | 48 |
|
21 |
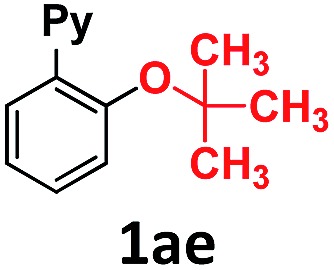
| 8 | t-BuONa | tert-Butanol | 48 |
|
4 |
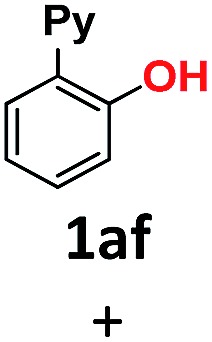
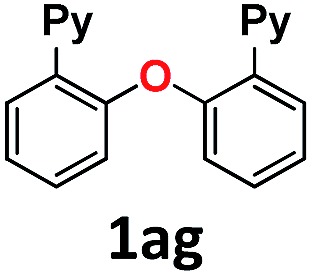
| 9 | HONa | H2O | 24 |
|
34 (1af), 26 (1ag) |
| 10 | MeONa | H2O | 24 |
|
52 (1af), 21 (1ag) |
aGeneral conditions: [2-(2-halophenyl)pyridine] = 20 mM, [alkoxide] = 40 mM, 0.5 mL solvent, 110 °C.
bCalculated with 1H-NMR spectroscopy using 1,3,5-trimethoxybenzene as the internal standard.
c Ref. 11.
dIn parentheses, the yield of the ethoxide insertion product.
eIn parentheses, the yield after 48 h.
fThe alkoxide was generated in situ adding 2 equivalents of sodium tert-butoxide as a base.
