Figure 2.
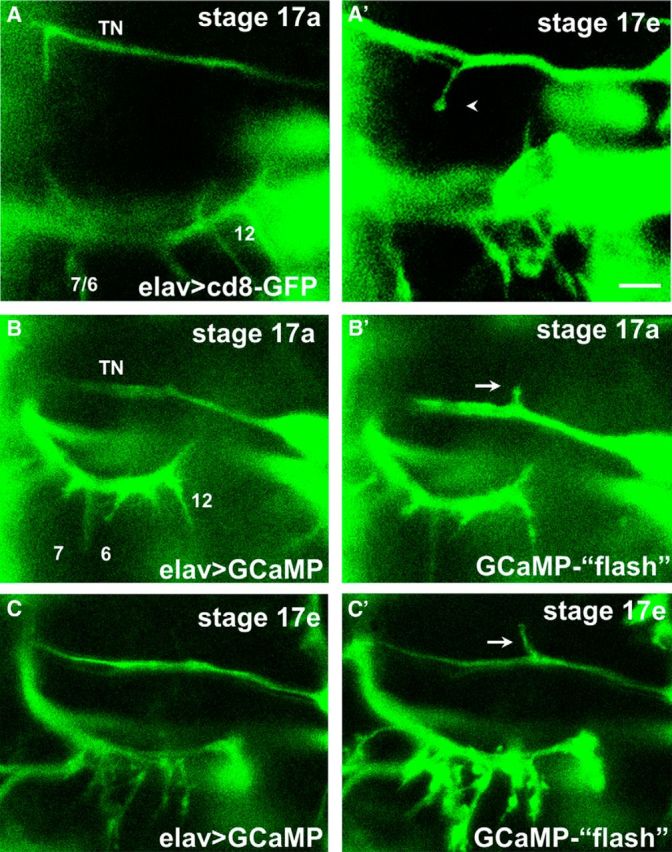
In vivo imaging of ectopic contacts during embryogenesis reveals the formation of bouton-like structures and intracellular Ca2+ signals. A, A′, Time-lapse images of the formation of an ectopic contact on muscle 6 in an intact embryo expressing CD8-GFP pan-neurally. At early stages (Stage 17a, ∼16.5 h AEL, A), a prominent filopodium formed from the TN. Several hours later (Stage 17e, A′), motile filopodia are no longer observed, and an ectopic branch on muscle 6 that failed to retract showed bouton-like morphology (arrow). Scale bar, 5 μm. B, C, Motoneuron filopodia and terminals from the TN and SNb nerves at two different stages in the same animal. Changes of intracellular Ca2+ are revealed by increases in GCaMP fluorescence (“flashes,” B′, C′) compared with the basal fluorescence (B, C). Ca2+ signals are observed in ectopic filopodia branching off the TN (arrows) at early (B′) stages of embryogenesis when most motoneuron growth cones are motile, as well as at late stages (8 h later, C′) when native SNb terminals showed bouton-like structures.
