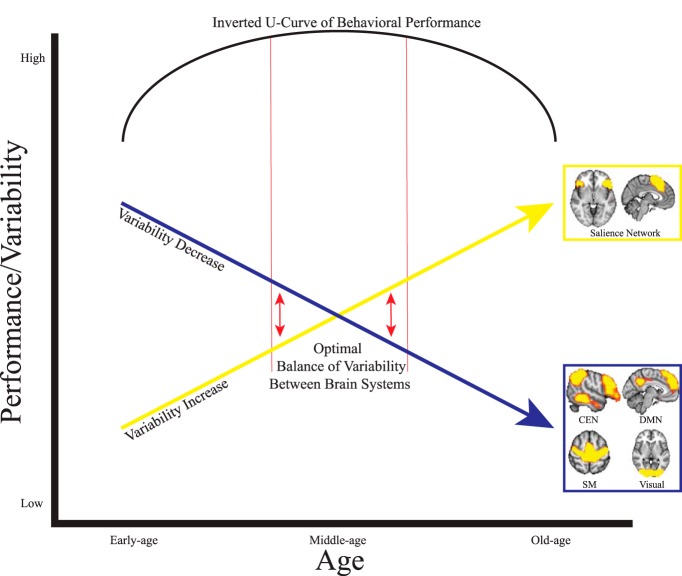
Figure 6.
Speculative model describing the proposed relationship between linear increases and decreases in BOLD variability across the lifespan and the inverted U-shaped curve of lifespan behavioral performance characterizing many behavioral tasks. The yellow arrow indicates linear increases in BOLD variability for SN nodes and the blue arrow indicates linear decreases in BOLD variability for CEN, DMN, sensorimotor (SM), and visual areas. In early and old age, large differences in variability between brain networks leads to suboptimal behavioral performance. The red arrows indicate that optimal behavioral performance may come from the intrinsic balance between high and low variability between different brain networks in middle age.