Figure 2.
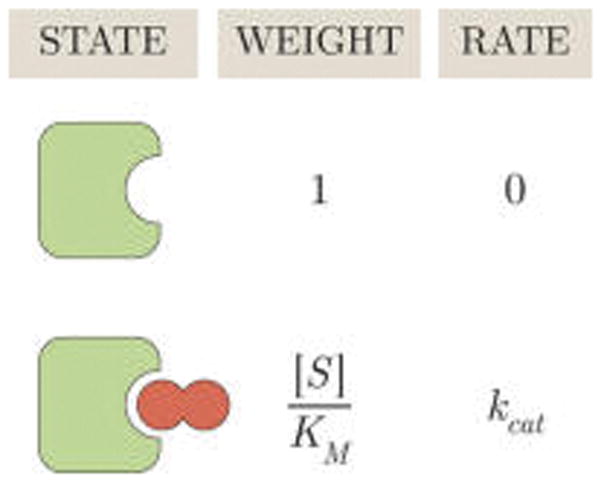
States and weights for the Michaelis–Menten enzyme. Each enzyme conformation is shown together with its weight and its catalytic rate. The probability of finding an enzyme (green) in either the free or bound state equals the weight of that state divided by the sum of all weights ( ) where [S] is the concentration of substrate (dark red) and is the Michaelis constant. At [S] = KM, half of the enzyme population exists in the free form and half exists in the bound form. For [S] > KM, more than half of all enzymes will be bound to substrate.
