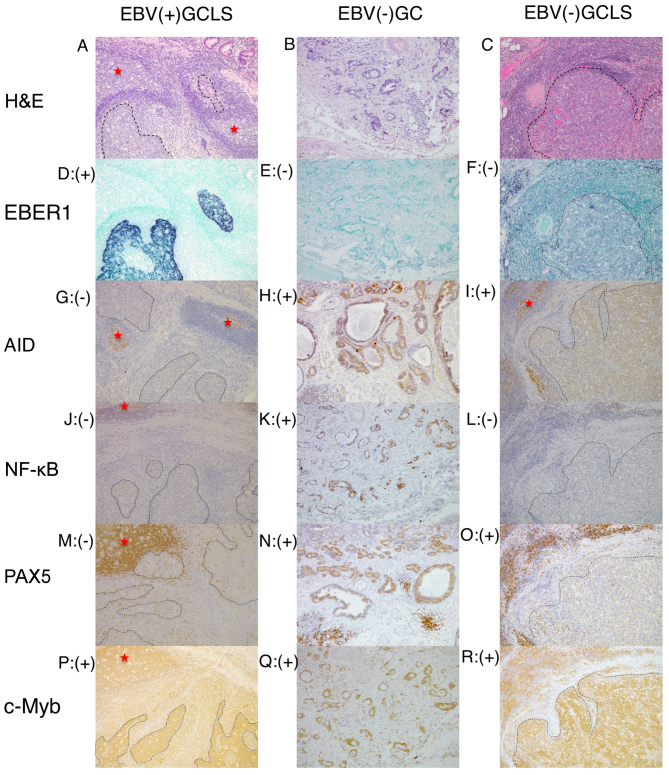
Figure 1.
Representative histology, ISH and immunostaining images of EBV(+) GCLS, EBV(−) GC without LS and EBV(−) GCLS. H&E staining of (A) EBV(+) GCLS, (B) EBV(−) GC without LS and (C) EBV(−) GCLS. EBER1 ISH of (D) EBV(+) GCLS, (E) EBV(−) GC without LS and (F) EBV(−) GCLS. AID immunostaining of (G) EBV(+) GCLS, (H) EBV(−) GC without LS and (I) EBV(−) GCLS. NF-κB immunostaining of (J) EBV(+) GCLS, (K) EBV(−) GC without LS and (L) EBV(−) GCLS. PAX5 immunostaining of (M) EBV(+) GCLS, (N) EBV(−) GC without LS and (O) EBV(−) GCLS. c-Myb immunostaining of (P) EBV(+) GCLS, (Q) EBV(−) GC without LS and (R) EBV(−) GCLS. Magnification, ×100. (G, I) Red stars indicate AID expression as the positive internal control observed in the lymphoid cells of the germinal center. ISH, in situ hybridization; EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; GCLS, GC with LS; GC, gastric carcinoma; LS, lymphoid stroma; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; EBER1, EBV-encoded small RNA 1; AID, activation-induced cytidine deaminase; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; PAX5, paired box 5; c-Myb, c-Myb proto-oncogene.