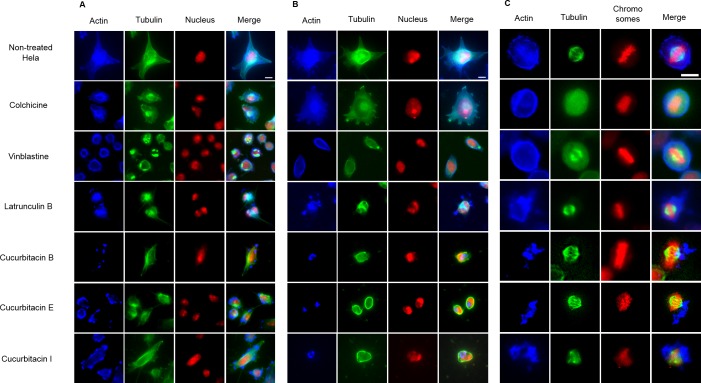
Figure 3. The effects of cucurbitacins on Hela mitotic cells using immunofluorescence staining.
Microtubules & mitotic spindles were stained by mouse anti-α-tubulin monoclonal IgG and goat anti-mouse IgM-FITC (green), actin filaments were stained by Atto 390 phalloidin (blue) and nucleus & chromosomes were stained by propidium iodide (red). (A) and (B) show immunofluorescence micrographs of Hela interphase cells treated for 1 h and 24 h with all six compounds at the concentration of IC80. Known tubulin inhibitors colchicine and vinblastine induced microtubule depolymerization and tubulin paracrystals, respectively. Actin-binding agent latrunculin B caused the rapid change of cell morphology and depolymerization of actin filaments. Cucurbitacins changed the morphology of microtubule network and caused actin aggregation. (C) shows immunofluorescence micrographs of Hela metaphase cells treated for 24 h with all six compounds at the concentration of IC50. Absent spindle and depolymerized bipolar spindles were caused by colchicine and vinblastine, respectively. Latrunculin B depolymerized actin filaments without alternating spindles and chromosomes arrangement. Cucurbitacins altered mitotic spindles and induced actin depolymerization and aggregation. Bar = 10 µm.