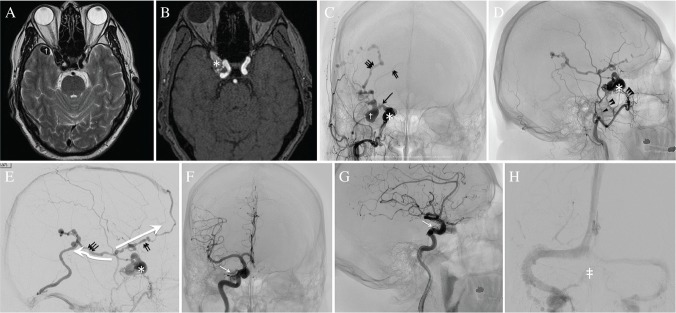
Fig. 1.
MR images (A, B), external carotid angiograms (C–E) and internal carotid angiograms (F–H) before endovascular treatment. A T2-weighted (A) and time-of-flight (B) MR images show a varix (dagger) in the right middle cranial fossa and dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF) in a lesion at a lateral location of the cavernous sinus (asterisk). (C, D, E) The right external carotid angiogram (ECAG) reveals a DAVF in a sinus of the lesser sphenoid wing (SLSW) (asterisk), the retrograde leptomeningeal venous drainage (RLVD) with the varix (dagger) and cortical venous ectasia, and three main feeders; middle meningeal artery (arrowhead), the accessory meningeal artery (double arrowhead), and artery of the foramen rotundum (triple arrowhead). The right ECAG in the late venous phase shows the RLVD from the isolated SLSW to the deep middle cerebral vein (DMCV) via a bridging vein (arrow). The RLVD from the DMCV is drained into two routes (large white arrows), comprising the frontal cortical vein (double arrow) and posterior insular vein (triple arrow) with venous ectasia. The frontal cortical vein is connected to the superior sagittal sinus. The posterior insular vein is finally drained into the transverse sinus through the temporal cortical vein. (F, G) The right ICAG in the arterial phase shows some small feeders from the meningohypophyseal trunk and ophthalmic artery (white arrow). (H) The right ICAG in the venous phase reveals the patent right cavernous sinus (double dagger) and inferior petrosal sinus.