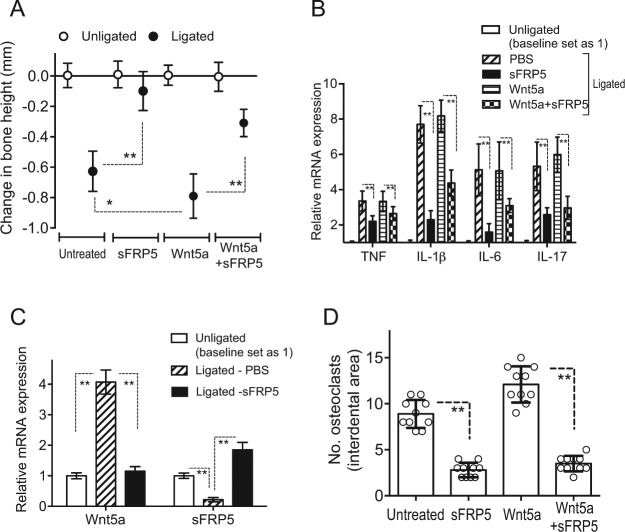
Figure 5.
Secreted frizzled-related protein 5 (sFRP5) inhibits ligature-induced periodontitis. (A) Periodontal bone loss was induced for 5 d in mice by ligating a maxillary second molar and leaving the contralateral tooth unligated (baseline control). Groups of mice were locally microinjected into the palatal gingiva with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; control), Wnt5a (0.2 µg), sFRP5 (0.2 µg), or their combination 1 d before placing the ligature and every day thereafter until the day before sacrifice (day 5). (B) In the same mice, ligature-induced periodontal inflammation was monitored in dissected gingiva processed for quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) to determine messenger RNA (mRNA) expression of the indicated cytokines. (C) In a similar ligature-induced periodontitis study where the mice were microinjected with PBS (control) or with sFRP5 (0.2 µg), dissected gingiva were processed and subjected to qPCR to determine the effect of sFRP5 on the mRNA expression of Wnt5a and sFRP5. In B and C, the data were normalized against glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase mRNA and expressed as fold change in the transcript levels in the ligated side relative to those of the unligated side, assigned an average value of 1. Data are means ± SD (A and B, n = 10 including 5 female and 5 male mice; C, n = 6 including 3 female and 3 male mice). (D) In a replica experiment as in A, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP)-positive multinucleated cells (osteoclasts) were enumerated from 2 random coronal sections of the ligated molar from each of 5 male mice and averaged with the SD from the total 10 sections/group. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 between indicated groups.