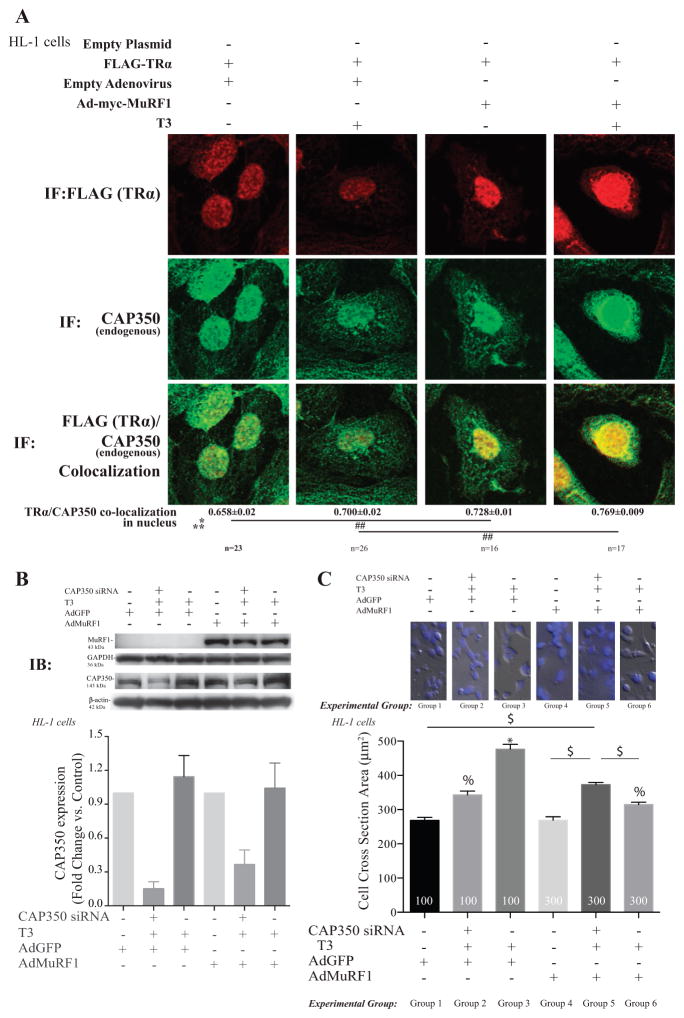
Figure 6.
MuRF1 inhibition of T3-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy is dependent on the centrosome-associated protein 350 (CAP350). (A) Confocal immunofluorescent images of TRα (anti-FLAG, red) and CAP350 (green) in cells transduced/transfected with vectors indicated and treated with T3 for 2 h (Fig. 3 for fluorescence controls). Data are reported as the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 3 independent experiments). A two-way ANOVA test was used to determine statistical significance. *Significance on the level of adenovirus group, **Significance on the level of treatment group. Significance between groups is represented as ##P < 0.001 as determined using a pairwise post-test. (B) Knock down of CAP350 in HL1 cardiomyocytes using siRNA achieved >50% reduction in protein by immunoblot analysis. (C) Cell cross-sectional area analysis of T3-stimulated HL-1 cells with increased MuRF1 (AdMuRF1) and CAP350 knock-down to identify the role of CAP350 in MuRF1-mediated inhibition of T3-induced hypertrophy. Data are reported as the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 2 independent experiments). A one-way ANOVA test was used to determine statistical significance. Significance between groups is represented as *P < 0.05 vs all other groups, % P < 0.05 vs groups 1, 4, and $P < 0.05 in indicated comparisons, 400× final magnification.