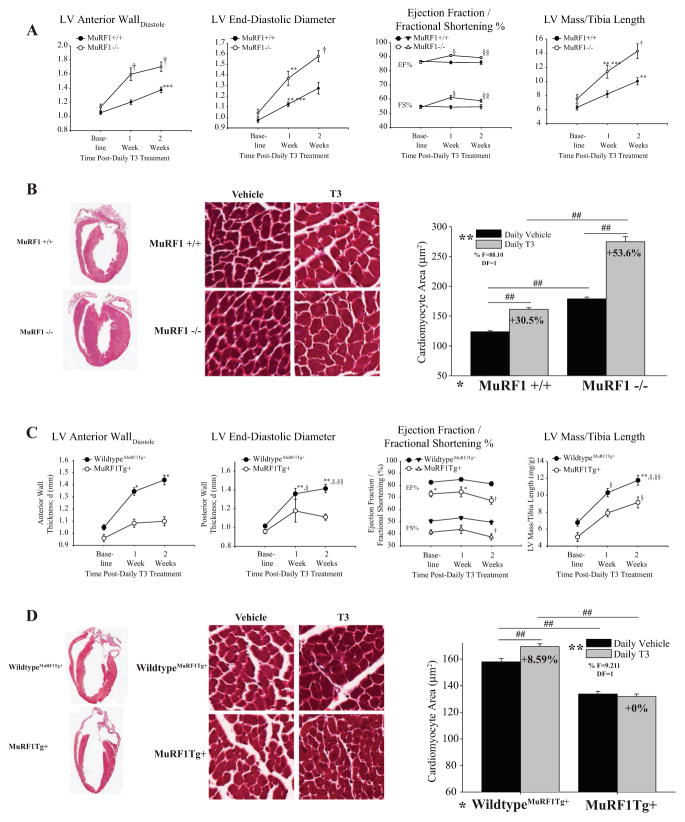
Figure 8.
MuRF1’s attenuation of TRα activity is identified in both MuRF1−/− and cardiac (αMHC)-MuRF1Tg+ mice in vivo after T3 stimulation. (A) Conscious echocardiographic data from wild-type (MuRF1+/+) and knockout (MuRF1−/−) receiving daily T3 i.p. (vehicle control = PBS) for 2 weeks (Table 1 for complete complementary echocardiographic data). (B) Gross and histological analysis of H&E and Masson’s trichrome hearts (100× magnification) from T3-treated MuRF1−/− mice. (C) Echocardiographic data from T3-treated wild-type MuRF1Tg+ and MuRF1Tg+ (Table 2 for complete complementary echocardiographic data). (D) Gross and histological analysis of H&E and Masson’s trichrome hearts (100× magnification) from T3-treated MuRF1Tg+ mice. A two-way ANOVA test was used to determine statistical significance using a pairwise post-test. For echocardiographic data: †P < 0.001 vs all other groups, ***P < 0.001 vs matched wild type, **P < 0.001 vs MuRF1+/+ and MuRF1−/− baseline; §P < 0.001 vs all other groups except MuRF1−/− +T3 at 2 weeks, §§P < 0.001 vs all other groups except MuRF1−/− +T3 at 1 week. Data on cardiomyocyte area were generated from three mice per group by averaging values from 400 cardiomyocytes per animal and statistical significance between indicated groups is designated by #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.001. The F statistic and degrees of freedom (DF) were reported when dependence between groups was found to be a significant source of variation, 20× final magnification.