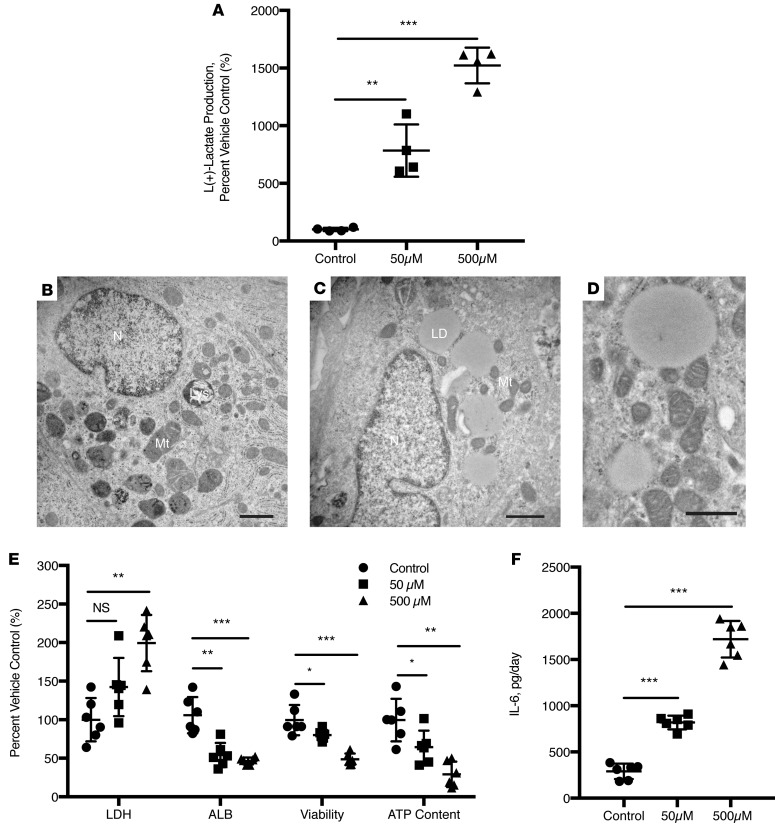
Figure 4. Engineered human liver tissues detect FIAU-induced toxicity associated with fatal human-specific liver injury.
Ten-day-old fetal total liver cells (FTLCs) in Col-I ICC were treated with the indicated concentrations of fialuridine (FIAU) or vehicle control for up to 14 days. (A) L(+)-lactate production by FTLCs was monitored in cultures after 4 days of treatment with the indicated concentrations of FIAU (n = 4). Ultrastructural images of (B) vehicle only and (C) FIAU-treated hepatocytes with abundant large lipid droplets. N, nucleus; Mt, mitochondria; LD, lipid droplet; Lys, lysosome. Scale bars: 1 μm. (D) Higher-power image of FIAU treatment group highlights mitochondrial damage and formation of large lipid droplets. Scale bar: 0.5 μm. (E) Cytotoxicity (LDH leakage), albumin production, cell viability, and ATP content of the cultures were assessed at the end of 14 days after FIAU treatment (n = 6). (F) FIAU-treated cultures demonstrated significant production of IL-6 in a dose-dependent manner following 2 days of FIAU treatment. All data was normalized to their respective vehicle-only controls. Statistical significance was analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett post test. *P < 0.0332, **P < 0.0002, ***P < 0.0001.