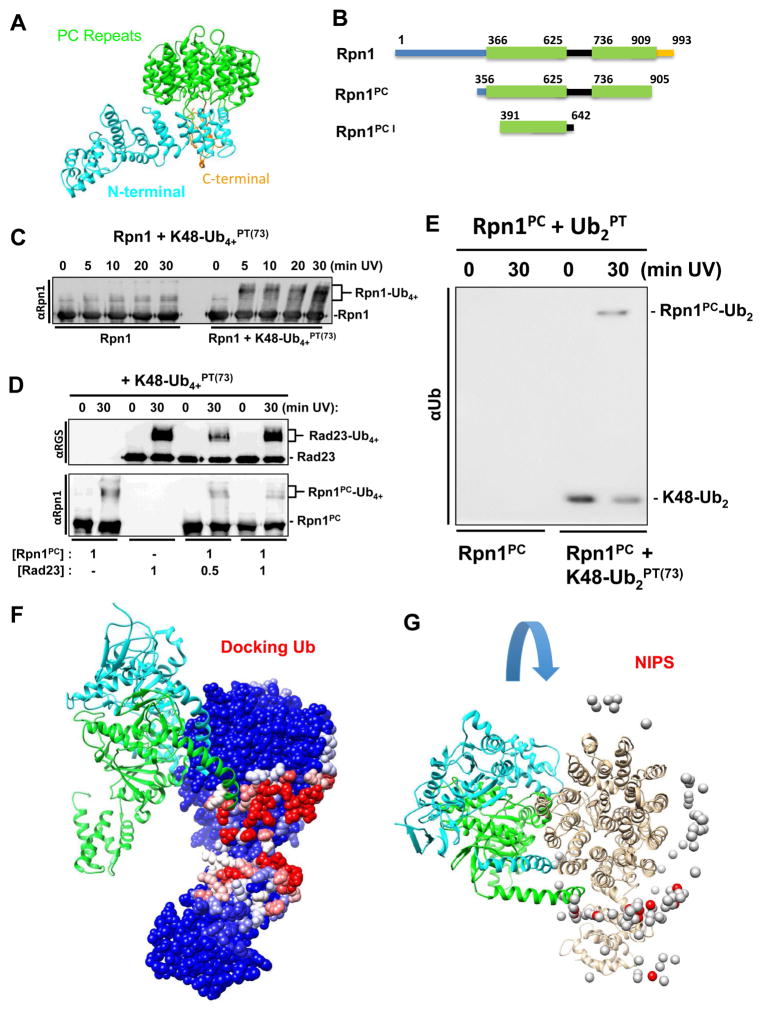
Figure 4.
(A) Rpn1 structure from PDB 4CR2 (chain Z) with PC repeats (green), N-terminal region (cyan), and flexible linker (gold). (B) Schematic dissection of Rpn1 domains used in the study (PC repeats in green). C) Time course of crosslinking of K48-Ub4+PT(73) and full-length Rpn1. (E) K48-linked diUbPT(73) was crosslinked to Rpn1PC (Rpn1356–905). (D) K48-Ub4+PT(73) successfully crosslinks with Rad23 alone and in varying concentrations of Rpn1PC (top). Unexpected crosslinking products of K48-Ub4+PT(73) and Rpn1PC are uncovered with anti-Rpn1 (bottom). (F) Molecular docking analysis using PDB 4CR2 for the Rpn1 structure and the PDB 1UBQ for ubiquitin. The position of two nearest neighbors in the 19S, Rpt1 and Rpt2, are shown in light blue and green respectively according to the EM model. (G) Rpn1 colored by NIP values (see methods, higher values in red) in the context of the proteasome with its interacting subunits. 26S protease regulatory subunit 7 homologs (Rpt1, chain H, colored cyan) and 26S protease regulatory subunit 4 homolog (Rpt6, chain I, colored green). Ub docking does not interfere with binding of RPN1 to the proteasome.