Figure 3.
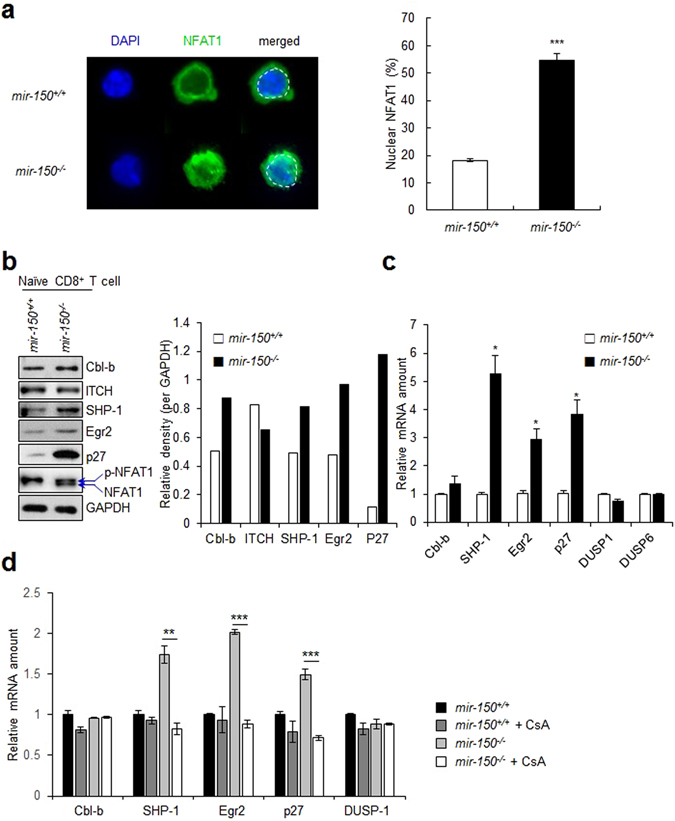
miR-150 deficiency induces the expression of anergy-related genes in naïve CD8+ T cells. (a) The level of nuclear localization of NFAT1 in mir-150 +/+ and mir-150 −/− naïve CD8+ T cells after incubation under Ca2+ (2 mM) for at 20 min. The images are the representative samples (left) and the level of nuclear localization of NFAT1 (right). (b) The expression level of anergy-related genes and phosphorylation status of NFAT1 in naïve mir-150 +/+ and mir-150 −/− CD8+ T cells after incubation in 2 mM Ca2+ containing media (left) and the calculated expression levels (right). Western data are the cropped blot images representing indicated proteins. (c) Relative expression level of anergy-related and Egr2-related gene in mRNA levels in mir-150 −/− naïve CD8+ T cells compared with those in mir-150 +/+ naïve CD8+ T cells. (d) The effect of inhibition of NFAT translocation on the expression levels of anergy-related genes in mir-150 +/+ and mir-150 −/− naïve CD8+ T cells. Isolated mir-150 +/+ and mir-150 −/− naïve CD8+ T cells were incubated with or without cyclosporine A (CsA, 3 µM) for 12 h and the amount of anergy-related mRNAs were measured using RT-PCR *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Data are means ± SEM of duplicate triplicate samples from a single experiment and are representative of two independent experiments.
