Figure 1.
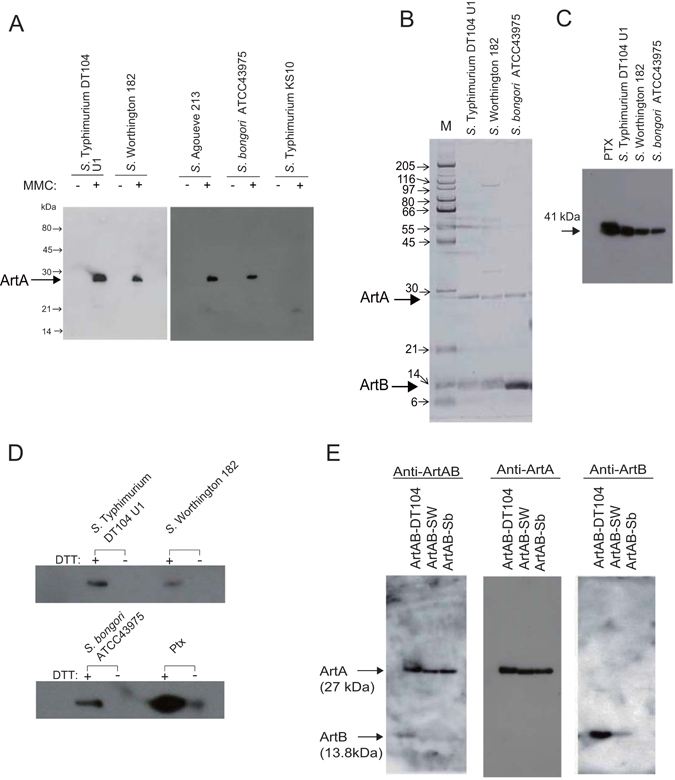
Expression and purification of ArtABs. (A) Induction of ArtA expression in Salmonella strains by treatment with mitomycin C (MMC). Overnight cultures grown in syncase broth with ( + ) or without (−) 0.5 μg/ml MMC were centrifuged to separate the cells. The supernatant was passed through a 0.22-μm filter, and concentrated 15-fold using a Vivaspin 10 K (GE Healthcare). Total protein contents from the supernatants of S. Typhimurium DT104 strain U1, S. Worthington strain 182, S. Agoueve strain 213, S. bongori strain ATCC43975, and S. Typhimurium strain KST10 were resolved by SDS-PAGE and probed with an antibody against the 14-a.a. peptide corresponding to the Arg10–His23 sequence of S. Typhimurium DT104 ArtA. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis of purified ArtABs from Salmonella strains. Purified ArtAB from S. Typhimurium DT104 stain U1, S. Worthington strain 182, and S. bongori ATCC43975. The gel was stained using a silver staining kit. (C,D) ADP-ribosylation of Ptx-sensitive G proteins by ArtABs; Ptx-sensitive G proteins from bovine brain (0.1 μg) were incubated with biotinylated NAD and purified ArtABs (100 ng) isolated from the indicated strain for 1 h at 37 °C, and then ADP-ribosylated proteins were analysed by 12.5% SDS-PAGE (C), and ADP-ribosylation in the presence or absence of 20 mM DTT (D). (E) Western blot analysis of purified ArtABs. ArtAB-DT104, ArtAB-SW, and ArtAB-Sb were probed with rabbit anti-ArtAB, anti-ArtA, and anti-ArtB antibodies.
