Figure 5.
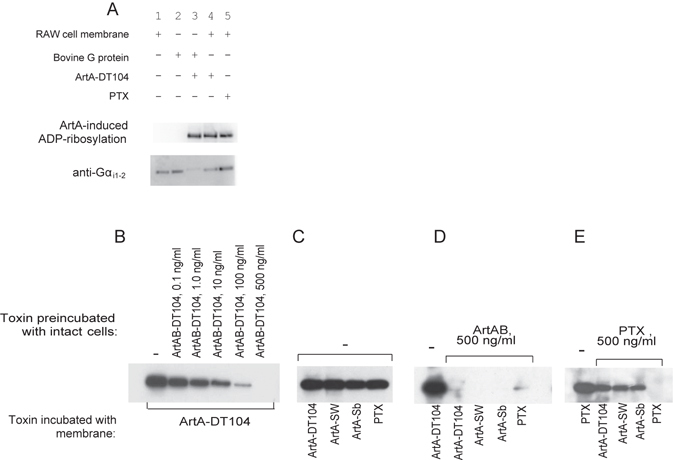
ArtABs catalyse ADP-ribosylation of G proteins in RAW 264.7 cells. (A) ADP-ribosylation of G proteins by ArtA-DT104. Upper panel, western blot showing biotin-ADP ribose labelling of Ptx-sensitive G proteins from the bovine brain and RAW 264.7 cell membranes (3.6 μg) by ArtA-DT104 expressed in vitro (2 μl) or Ptx (100 ng), in the presence of biotin-NAD. Samples were resolved by 12.5% SDS-PAGE, and ADP-ribosylated proteins were detected by western blotting using peroxidase-conjugated streptavidin as described in Materials and Methods. Lower panel, western blot of the RAW 264.7 cell membrane fraction probed with anti-Gαi1 and -Gαi2 IgG antibodies. Lane 1, membrane fraction of RAW 264.7 cells; lane 2, Bovine G proteins; lane 3, Ptx-sensitive G proteins from the bovine brain incubated with ArtA expressed in vitro; lane 4, RAW 264.7 cell membranes incubated with in vitro-expressed ArtA-DT104; lane 5, RAW 264.7 cell membranes incubated with Ptx. (B–E) In vitro ADP-ribosylation of cell membrane proteins after preincubation of RAW 264.7 cells with ArtAB-DT104 or Ptx. RAW 264.7 cells were incubated with the toxins indicated in upper row (Toxin preincubated with intact cells) for 16 h at 37 °C, and then cell membranes were prepared. The membranes from the pretreated cells were then incubated with the toxins indicated in bottom row (Toxin incubated with membrane; in vitro-expressed ArtA or Ptx) in the presence of biotin-NAD. ADP-ribosylated proteins were detected by western blotting as described above. Results are shown for cells preincubated with different concentrations of ArtAB-DT104 (B); with no toxin pre-treatment (C); with 500 ng of ArtAB-DT104 (D); and with 500 ng of Ptx (E). In the bottom row, toxin with membrane indicates which toxin was added along with biotinylated NAD to the membrane fractions during the in vitro membrane labelling.
