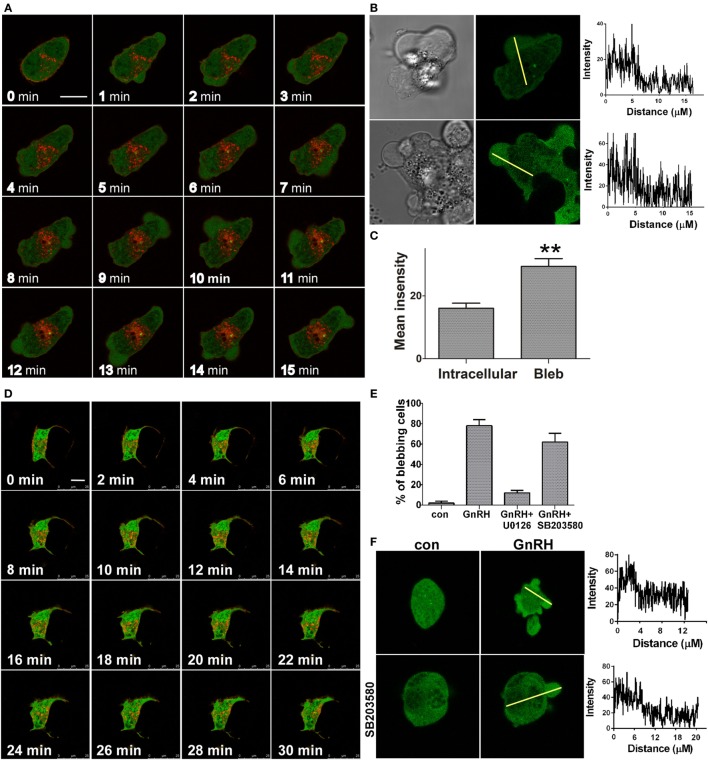
Figure 3.
ERK1/2 is present and involved in bleb formation. (A) Addition of GnRH (0–15 min, 10 nM) to serum-starved LβT2 cells transfected with GnRH receptor (GnRHR)-mCherry and ERK-GFP resulted in bleb formation, while ERK1/2 accumulates in the blebs. The scale bar is 10 µm. (B) Blebs images after GnRH treatment including differential interference contrast (DIC) and fluorescent images of ERK2-GFP. A line intensity profile across the cells was obtained and intensity profiles are shown on the right. (C) Bars show mean ± SEM of fluorescence intensity of the blebs vs. intracellular area from multiple scanning of each cell from at least five experiments. **p-Value ≤0.01. (D) Addition of the MEK selective inhibitor U0126 (25 µM) 20 min prior to GnRH (0–30 min, 10 nM) to serum-starved LβT2 gonadotrope cells transfected with GnRHR-mCherry and ERK2-GFP abolished bleb formation. Similar results were observed in two other experiments. The scale bar is 10 µm. (E) ERK1/2, but not p38MAPK, is involved in bleb formation. Serum-starved LβT2 gonadotrope cells were pretreated with U0126 or SB203580 (MEK and p38MAPK selective inhibitors, respectively) at 25 µM for 20 min prior to GnRH (10 nM, 30 min). Quantitation of the percentage of blebbing cells is shown. Images of at least 10 fields were taken for each treatment, and the bars are mean ± SEM from 3 experiments. (F) Pretreatment with SB203580 did not attenuate GnRH-induced ERK1/2 accumulation in the blebs as indicated by fluorescence intensity measurements. Serum-starved LβT2 cells transfected with ERK-GFP and were pretreated with or without SB203580 (25 µM) for 20 min prior to GnRH (10 nM, 30 min). A line intensity profile across the cells was obtained, and intensity profiles are shown on the right.