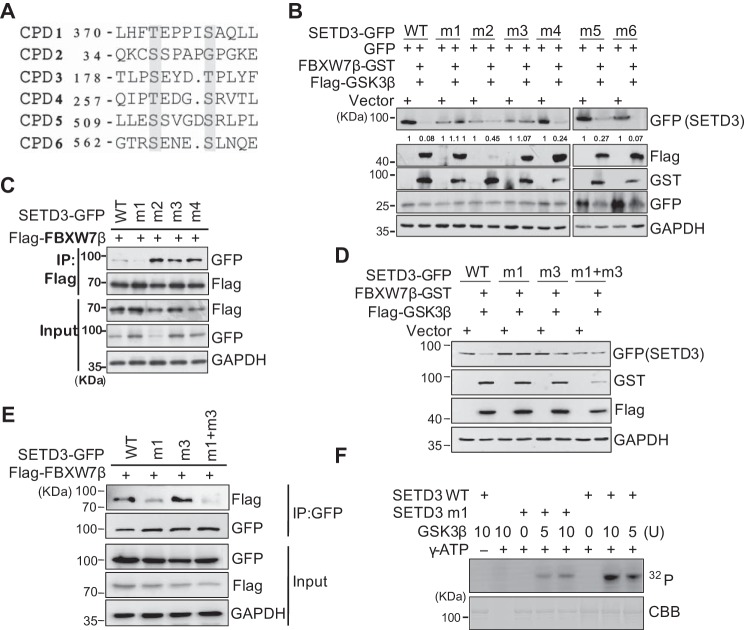
Figure 4.
CPD motif is required for SETD3 degradation. A, alignment of six putative CPD sequences in SETD3. The numbers represent the first amino acid position, and the amino acids in red indicate the ones mutated to alanine. B, wild-type or six putative CPD mutants of SETD3-GFP (named m1–m6) were co-transfected with either the empty vector or FBXW7β and GSKβ accompanied by the GFP vector in 293T cells. SETD3 protein levels were analyzed by Western blotting. C, wild-type or four CPD mutants (m1–m4) of SETD3-GFP were co-transfected with FLAG-FBXW7β in 293T cells. FBXW7β was subjected to IP with α-FLAG, and associated SETD3-GFP proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with α-GFP. D and E, double CPD mutant of SETD3 (m1 + m3) was examined by protein stability (D) or binding with FBXW7β (E), compared with wild-type or single mutants. F, in vitro kinase assays were performed using recombinant wild-type (WT) or a CPD1 mutant (m1) of GST-SETD3 incubated with different doses of GSK3β protein in the presence or absence of 32P-labeled γ-ATP. The phosphorylation signals of SETD3 were examined by autoradiography. The amounts of SETD3 protein used in each reaction were monitored by Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining (CBB).