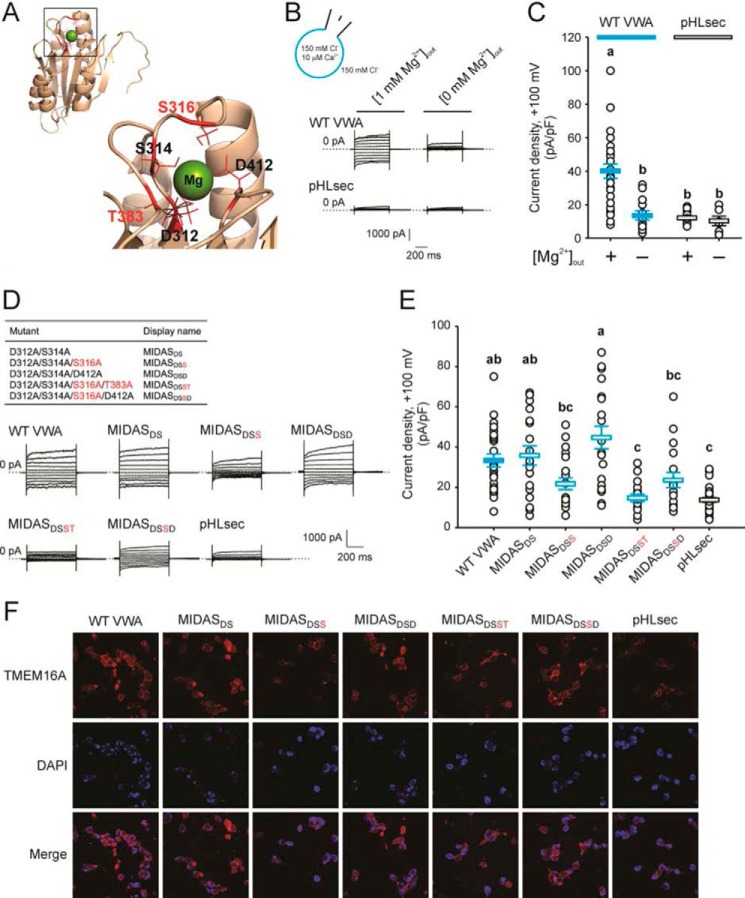
Figure 3.
A MIDAS motif within the CLCA1 VWA domain is implicated in the CLCA1-TMEM16A interactions. A, homology model of the CLCA1 VWA domain based on the VWA domain of C. acidiphila (PDB code 4FX5). Inset, the MIDAS pocket with an Mg2+ ion within. The critical residues Ser-316 and Thr-383 are highlighted in red. B and C, whole-cell currents measured in wild-type CLCA1 VWA- (WT VWA) or mock-conditioned (pHLsec) cells superfused with standard ([1 mm Mg2+]out) or Mg2+-free ([0 mm Mg2+]out) extracellular solution. D and E, whole-cell currents measured in mock-conditioned cells and in cells conditioned with WT or MIDAS motif mutant VWA superfused with standard extracellular solution. B and D, representative current traces displayed as in Fig. 1C. The pulse protocol is the same as in Figs. 1 and 2. The membrane capacitance was similar in all cases at ∼25 pF. C and E, current density at +100 mV. Symbols are data from individual cells (C, n = 6–25; E, n = 18–30); error bars indicate the means ± S.E. of all experiments. The results of the statistical analysis are indicated by lowercase letters; i.e. groups sharing letters are statistically similar (for example, groups labeled a and ab or groups labeled ab and bc), whereas those not sharing any letters are significantly different (for example, groups labeled a and b or groups labeled ab and c) (p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA; C, F = 13 and p = 3 × 10−9; E, F = 12 and p = 1 × 10−10; followed by Tukey test). F, immunofluorescence staining of TMEM16A (red) in pHLsec-, WT, or MIDAS motif mutant VWA-conditioned medium.