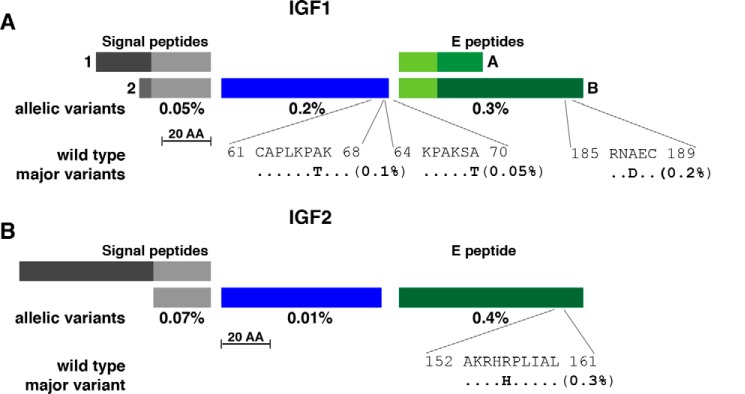
Figure 1.
Population variation in human IGF1 and IGF2. A, schematic of human IGF1 protein precursors, including two alternative signal peptides, a 70-residue mature IGF1 and the two COOH-terminal extension (E) peptides. Signal peptides 1 and 2 consist of 48 and 32 amino acids (AA), respectively, and E regions A and B of 35 and 77 residues, respectively, with the 16 NH2-terminal amino acids being identical. The overall population prevalence of variant alleles for each segment of pre-pro-IGF1 is listed below the map, and the location of the three most common variants is depicted in single-letter amino acid code. B, diagram of human IGF2 protein precursors, including alternative signal peptides, a 67-residue mature IGF2 and the COOH-terminal E peptide. The two signal peptides consist of 80 and 24 amino acids, respectively (the former has not been determined experimentally), and the E region is composed of 89 residues. The overall population prevalence of variant alleles for each segment of pre-pro-IGF2 is depicted below the map, and the location of the most common variant is shown. For A and B, the scale bar represents 20 amino acids.