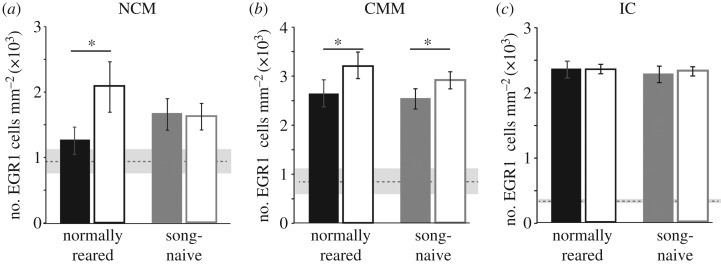
Figure 3.
EGR1 expression is differentially modulated by social context and developmental song exposure across brain areas. (a) In the NCM, EGR1 expression was modulated by the social context of the stimulus in normally reared females but not in song-naive females. *indicates a significant difference at p < 0.05. (b) In the CMM, EGR1 expression was significantly higher in response to courtship song than non-courtship song in both normally reared and song-naive females. *indicates significant effects of stimulus context but not rearing condition at p < 0.05. (c) In the IC, there were no effects of the social context of the stimulus on EGR1 expression in either normally reared or song-naive birds. Plotted are mean ± s.e.m. For all plots, open bars are responses to courtship song, filled bars are for non-courtship songs. Horizontal dashed lines with grey shading indicate the mean ± s.d. for EGR1 expression in silent controls.