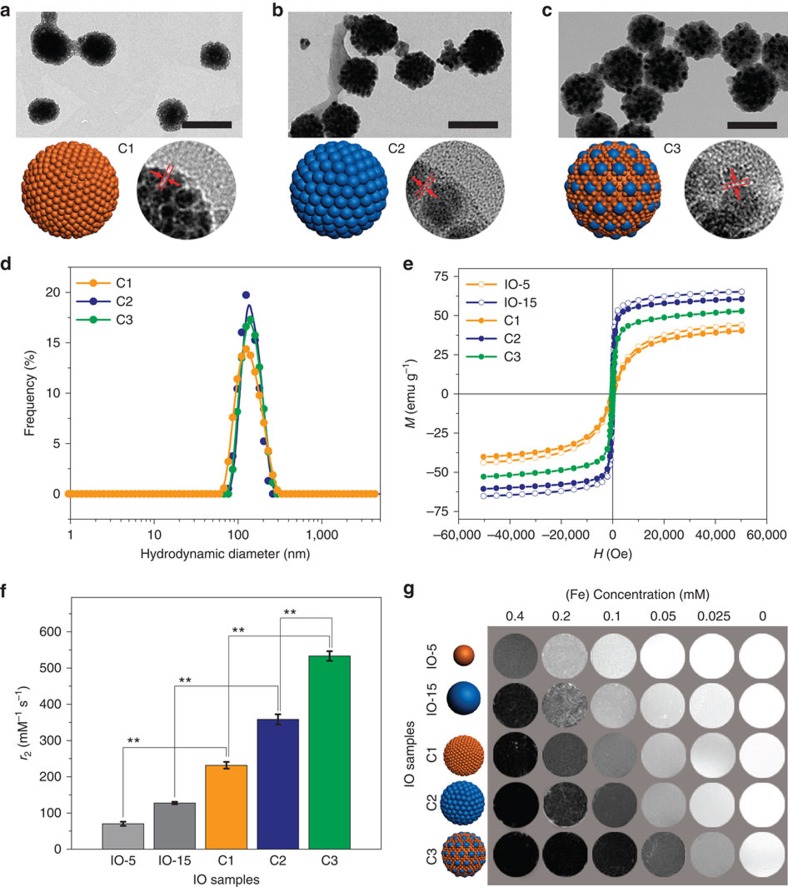
Figure 2. Iron oxide clusters C1–C3.
(a–c) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and high-resolution TEM images, as well as cartoons of iron oxide (IO) clusters C1–C3, respectively. Scale bars, 200 nm. The inter-particle distances (L) are around 1 nm. (d) Dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements indicate uniform hydrodynamic diameters of IO clusters C1–C3. (e) Magnetic hysteresis (M–H) curves of single IO-5 and IO-15 NPs, and IO clusters C1–C3 measured at 300 K. (f) Columns show r2 values of IO clusters C1–C3, as well as the single IO-5 and IO-15 NPs. Mean values±s.d.; n=3 (**P<0.01). (g) MR phantom of different IO samples show concentration- and relaxivity-dependent contrasts. Darker contrast indicates stronger T2 relaxation enhancement for each concentration. All MRI studies were conducted on a 7 T MRI scanner.