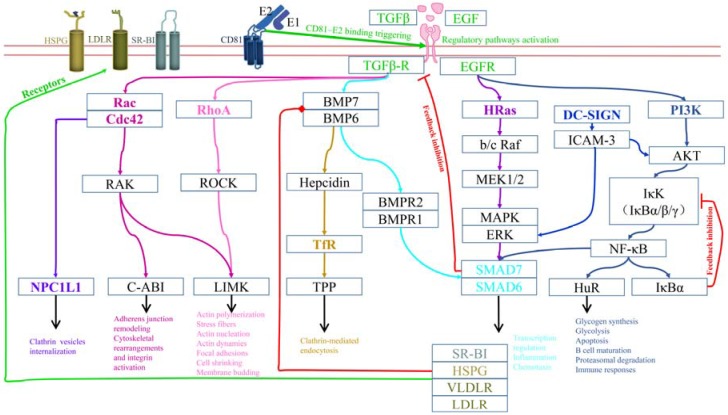
Figure 2.
A proposed regulatory signaling network for HCV entry. Signaling activation and entry receptors are indicated in the figure. Only the factors that are related to HCV entry are shown. Relationships between upstream and downstream factors are not limited to regulation; certain downstream factors may serve as a receptor for upstream factors. Specific colors indicate different pathways, while arrows and red lines indicate the main process of a pathway and an inhibitory feedback regulation, respectively. The outcome is shown at the end of each pathway. This network highlights that HCV entry is centrally regulated by EGFR and TGFβ-R. Abbreviations: NPC1L1, Niemann-Pick C1-like 1; Cdc42, cell division control protein 42 homolog; RhoA, Ras homolog gene family, member A; ROCK, Rho-associated protein kinase; LIMK, LIM domain kinase ; BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; BMPR, bone morphogenetic protein receptor; TfR, transferrin receptor 1; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; SMAD6/7, mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 6 and 7; DC-SIGN, dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule 3-grabbing nonintegrin; ICAM3, intercellular adhesion molecule 3; PI3K, phosphatidylinositide 3-kinases; AKT, protein kinase B (PKB); IκK, IκB kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; HuR, human antigen R; SR-BI, scavenger receptor class B type I.