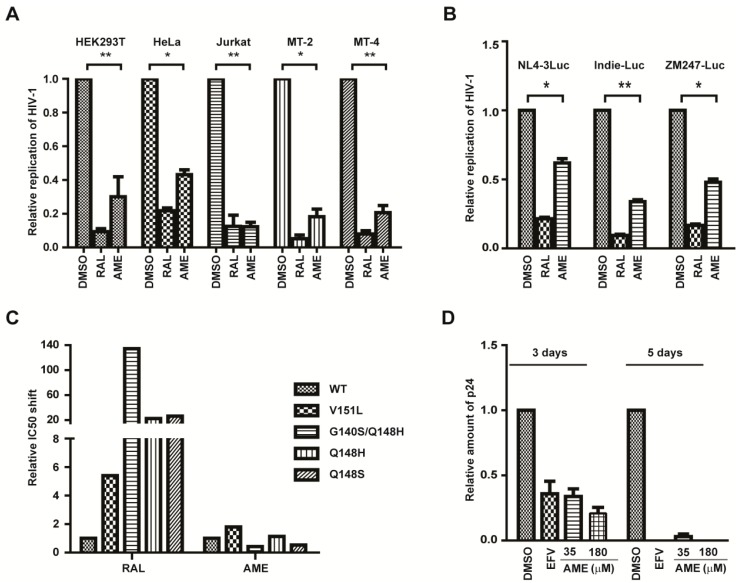
Figure 6.
AME inhibits the infection of different HIV-1 strains in different cell lines. (A) 5 × 105/mL Jurkat T, MT-2, MT-4, HeLa, and HEK293T cells were infected with VSV-G pseudotyped NL4-3Luc.R-E- viruses in the presence of DMSO, 25 nM RAL, and 60 µM AME. Forty-eight h post-infection, cells were harvested to measure luciferase activity; (B) SupT1 cells were infected with VSV-G pseudotyped subtype B NL4-3.luc.R-E- viruses, subtype C ZM247Fv1-Luc, or Indie-C1-Luc viruses treated with 12.5 nM RAL, 35 µM AME, or DMSO as the vehicle control. Two days post-infection, cells were harvested to measure luciferase activity; (C) SupT1 cells were infected with VSV-G pseudotyped NL4-3Luc.R-E- viruses or indicated RAL-resistant strains treated with AME, RAL, or DMSO at different concentrations. Cells were harvested to measure luciferase reporter activity. The IC50 for WT virus and RAL-resistant mutant virus was calculated; (D) Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were infected with wild type NL4-3 HIV viruses treated with 2 nM EFV, 35 µM or 180 µM AME, or DMSO. Supernatant were harvested to measure the quantity of p24 antigen by ELISA at day 3 and day 5. Data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.