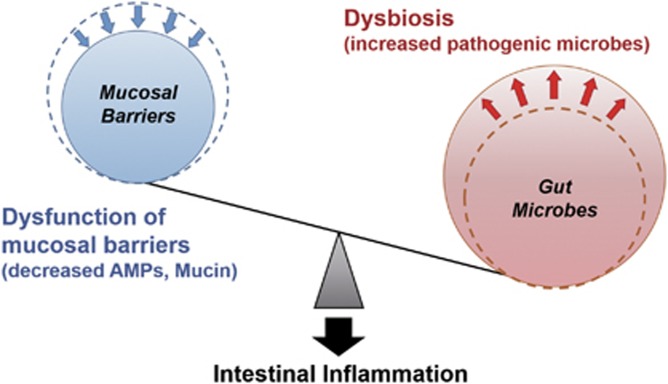
Figure 3.
The imbalance between mucosal barriers and gut microbes promotes susceptibility to intestinal inflammation. Dysfunction of mucosal barriers because of genetic predisposition, such as the decreased production of AMPs and mucin, allows intestinal bacteria to gain access to gut immune cells, thereby contributing to the development of intestinal inflammation. Dysbiosis induced by environmental factors, such as a high-fat diet and various medicines, accelerates intestinal inflammation in situations in which the mucosal barrier is disrupted. AMPs, antimicrobial peptides.