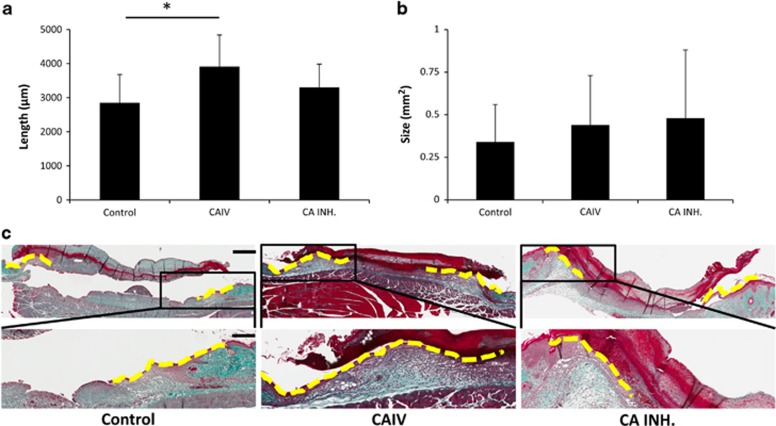
Figure 5.
Accelerated re-epithelialization during wound healing in mice treated with recombinant Car4 enzyme. Mice with full-thickness skin excision wounds were treated with either recombinant Car4 enzyme or CA inhibitor applied topically to the wound immediately after wounding. Scars were harvested on day 5, and the re-epithelialization (a) and cross-sectional area of the granulation tissue (b) of the wounds were quantified by examining two microscopic sections from each wound. The results are expressed as the average of the two values. There were five animals, each with two wounds, in every treatment group. *P<0.05; analysis of variance. The results are expressed as the mean±s.d., n=10 wounds. (c) Representative sections from wounds treated with recombinant CAIV or CA inhibitor and collected on day 5 after wounding are shown for re-epithelialization. Scale bars, 600 μm low magnification, 240 μm high magnification.