Figure 1.
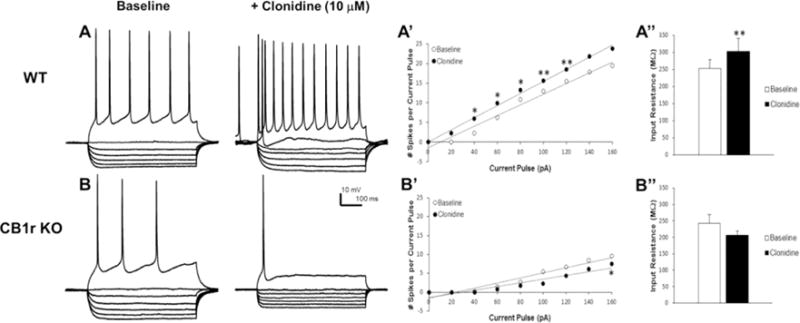
α2-adrenoceptor responses in mPFC pyramidal neurons in WT and CB1 receptor KO mice. Panels A and B indicate voltage responses to 700 ms current steps (pA; −100, −80, −60, − 40, −20, 0, +80) from a representative WT (A) and CB1 receptor KO mouse (B) both before and after bath application of clonidine (10 μM). Panels A’ and B’ summarize mean excitability data as stimulus-response curves to a range of current steps (0–160 pA) in mice from each genotype. Panels A” and B” show clonidine effects on membrane input resistance in mice from each genotype. Acute stimulation of the α2-adrenoceptor with clonidine increases excitability of mPFC neurons (A and rightward shift in A’) and increases input resistance (A”) in WT mice. In contrast, clonidine decreases excitability of mPFC neurons (B and leftward shift B’) and slightly decreases input resistance (B”) in CB1 receptor KO mice. Data represent mean ± SEM. Asterisks indicate a significant difference between baseline and clonidine by paired Student’s t-test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01).
