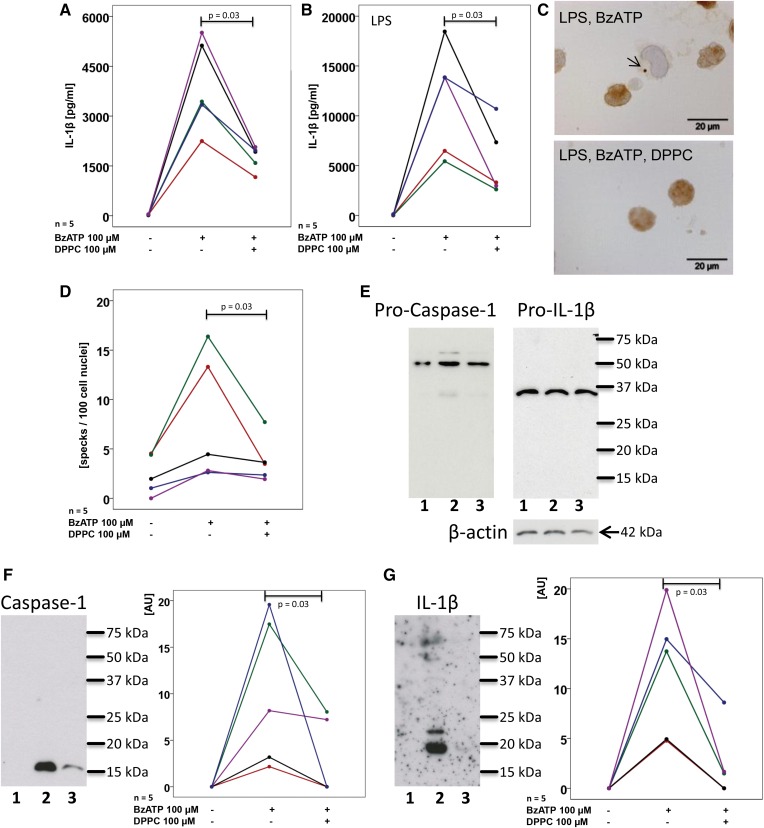
Fig. 3.
DPPC inhibits BzATP-mediated inflammasome activation in human PBMCs. PBMCs were isolated from healthy human donors, left untreated (A) or pulsed with LPS (B), cultured for 3 h and stimulated with BzATP in the presence or absence of DPPC. IL-1β levels were measured 30 min thereafter in cell culture supernatants. C, D: ASC specks were detected by immunocytochemistry in LPS-pulsed PBMC and stimulated with BzATP in the presence or absence of DPPC. C: Micrographs of PBMC: ASC immunopositive material is stained in brown, cell nuclei were lightly counterstained with hemalum, and the arrow is pointing to an ASC speck. D: The number of specks per 100 cell nuclei is depicted. E–G: PBMCs were pulsed with LPS (lane 1) and stimulated with BzATP in the absence (lane 2) or presence (lane 3) of DPPC and Western blots were performed with antibodies directed to human caspase-1, IL-1β, and β-actin. E: In cell lysates, exclusively, the pro-forms, pro-caspase-1 and pro-IL-1β, were detected; whereas, in concentrated cell culture supernatants, mature caspase-1 (F) and IL-1β (G) were detected. F, G: Immunopositive signals were quantified by densitometry and expressed as arbitrary units (AU). Data points obtained from individual blood donors are depicted and connected by lines. Data from the same individuals are coded by the same color in (A) and (B) as well as in (F) and (G), but in (A) and (B) a cohort of volunteers was investigated that was different than in (F) and (G). Wilcoxon sign rank test.