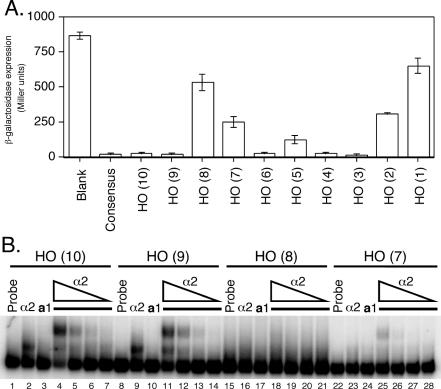
Figure 2.
Analysis of isolated HO a1-α2 sites reveals differential binding affinity. (A) β-galactosidase assay of heterologous CYC1-lacZ reporters with the indicated a1-α2 binding sites (x-axis) inserted between the UAS and TATA box of CYC1. Reporters were assayed in a MATa strain bearing a plasmid-based copy of MATα, with β-galactosidase expression (y-axis) indicated in Miller units (min−1 ml−1). (B) EMSAs using 32P-labeled oligonucleotide probes corresponding to the a1-α2 sites of URS1. Probes were incubated with either no protein (lanes 1, 8, 15 and 22), 8.2 × 10−9 M α2128–210 (lanes 2, 9, 16 and 23), or 2.8 × 10−9 M a166–126 (lanes 3, 10, 17 and 24). For lanes 4–7, 11–14, 18–21 and 25–28, a166–126 was kept at a constant concentration of 2.8 × 10−9 M, while α2128–210 was serially diluted 5-fold from 8.2 × 10−9 M (lanes 4, 11, 18 and 25) to 6.6 × 10−11 M (lanes 7, 14, 21 and 28).