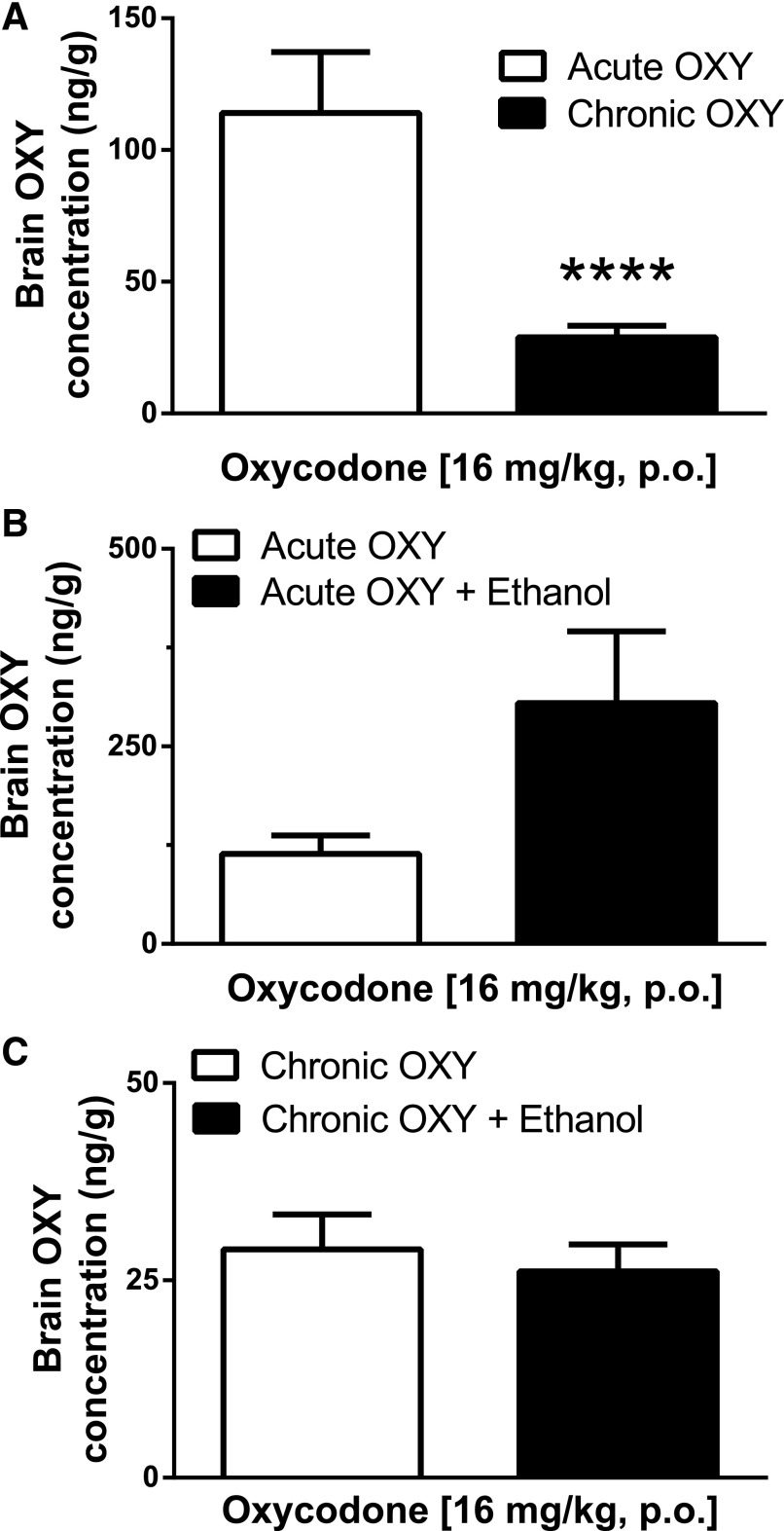
Fig. 5.
Acute and chronic oxycodone brain concentrations. (A) Oxycodone brain concentrations 20 minutes following a challenge gavage of oxycodone (16 mg/kg) in mice either naïve to oxycodone or chronically treated with oxycodone (64 mg/kg, PO) twice a day for 4 days. Acute concentrations represent the mean ± S.E.M. of 10 mice, whereas chronic concentrations represent the mean ± S.E.M. of 13 mice. Brain oxycodone concentrations detected 20 minutes following the oxycodone challenge were significantly lower in mice chronically treated with oxycodone compared with that of acutely treated mice (****P < 0.001, Student’s two-tailed unpaired t test). (B) The effects of ethanol (2 g/kg, PO) were assessed against acute oxycodone brain concentrations. Each bar represents the mean ± S.E.M. of at least 10 mice. Ethanol did not have a significant effect (P > 0.05, Student’s unpaired two-tailed t test), and both groups displayed similar brain oxycodone concentrations. (C) The effects of ethanol (2 g/kg, PO) were assessed against chronic oxycodone brain concentrations. Ethanol did not have a significant effect (P > 0.05, Student’s unpaired two tailed t test), and both groups displayed similar brain oxycodone concentrations in response to a challenge oxycodone gavage (16 mg/kg) following chronic oxycodone treatment. Each bar represents the mean ± S.E.M. of at least eight mice.