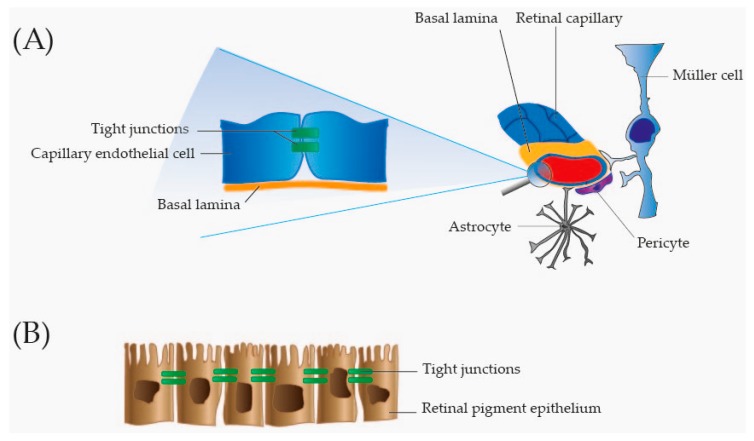
Figure 2.
Overview of the blood–retinal barrier. (A) Inner blood–retinal barrier. The inner blood–retinal barrier is formed by tightly adherent endothelial cells in the retinal capillaries. Tight junctions in the intercellular spaces keep the capillary endothelial cells tightly adherent. The endothelial cells rest on a basal lamina surrounded by pericytes, and foot processes of Müller cells and astrocytes. Pericytes, Müller cells and astrocytes are involved in the maintenance of the inner blood–retinal barrier; and (B) Outer retinal barrier. The outer blood–retinal barrier is secured through tight junctions between retinal pigment epithelial cells.