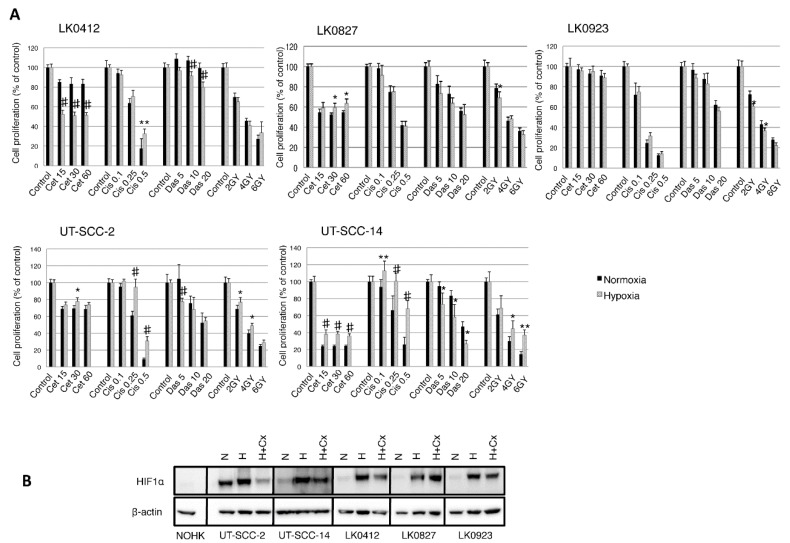
Figure 1.
Hypoxia-induced treatment response in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) cell lines. Cell lines were cultured in normoxia and hypoxia. (A) After 24 h, they were treated with various concentrations of cetuximab (cet; nM), cisplatin (cis; µg/mL), dasatinib (das; nM), and radiation (2, 4, 6 Gy). After 9 days the cytotoxic/cytostatic effect on cell proliferation was determined by crystal violet assay. Cell proliferation is presented as the percentage of the untreated controls (mean values ± SD; n = 3, triplicates). For statistical analysis, one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni analysis was used (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; # p < 0.001); (B) Western blot analysis of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α expression in normal oral human keratinocytes (NOHK) as well as UT-SCC-2, UT-SCC-14, LK0412, LK0827, and LK0923 HNSCC cells. Hypoxic cells were exposed to cetuximab (60 nM) for 3 days prior to harvesting for Western blotting; β-actin was used as the loading control. Abbreviations: N, normoxia; H, hypoxia; H + Cx, hypoxia in the presence of cetuximab; Cx, cetuximab.