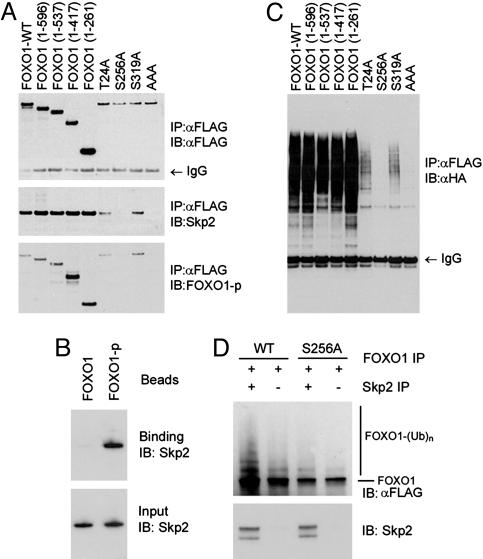
Fig. 3.
Interaction and ubiquitination of FOXO1 by Skp2 depend on phosphorylation of FOXO1 at Ser-256. (A) FOXO1 plasmids were cotransfected with Skp2 into LNCaP cells, and cell extracts were prepared for immunoprecipitation with an anti-FLAG antibody and immunoblotted with antibodies for FLAG, Skp2, or phospho-Ser-256 FOXO1 (FOXO1-p). (B) LNCaP cells were transfected with the indicated FOXO1, Skp2, and HA-tagged ubiquitin plasmids, and cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with the anti-FLAG antibody and immunoblotted with the anti-HA antibody. (C) Bacterially expressed GST-Skp2 was incubated in vitro with beads coupled to the FOXO1 phosphopeptide GKSPRRRAApSMDNNSKFAKS (FOXO1-p), which contains a phosphoserine at position 256. A corresponding nonphosphopeptide (FOXO1) was included as a control. (D) In vitro ubiquitination of FOXO1. Anti-FLAG immunoprecipitates immobilized on beads from LNCaP cells transfected with either wild-type (WT) or mutant (S256A) FLAG-FOXO1 were incubated with Skp2 proteins immunoprecipitated from Skp2-stable LNCaP cell lines (see Fig. 1) in a reaction system that contained 20 μM MG132 and rabbit reticulocyte lysate, which was precleared with anti-Skp2 antibody. Reactions were terminated by washing the pellets three times in RIPA buffer, and samples were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting.