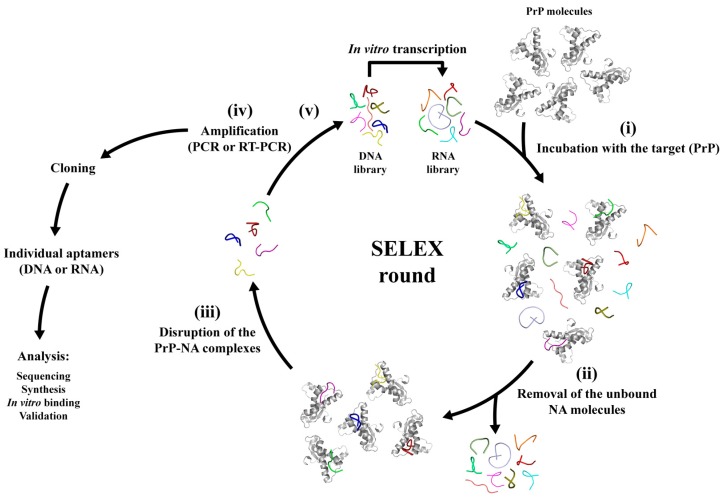
Figure 2.
General scheme of the SELEX method using recombinant PrP as the target. A SELEX round consists of the following essential steps: (i) binding after the incubation of a randomly synthesized DNA or RNA library (containing 1014–1016 different sequences) with the molecular target (full-length recombinant PrP or other PrP constructions); (ii) removal of the non-bound NA species; (iii) elution of NA sequences from the immobilized PrP (either in-column, in ELISA dishes, or other); (iv) amplification of the eluted NA sequences; (v) back to Step (i). This process can be repeated several times to enhance the affinity and specificity of the isolated NA sequences. The final selected NA pool contains the aptamers that have to be further cloned, and individual aptamers have to be sequenced and validated for binding against its target, PrP.