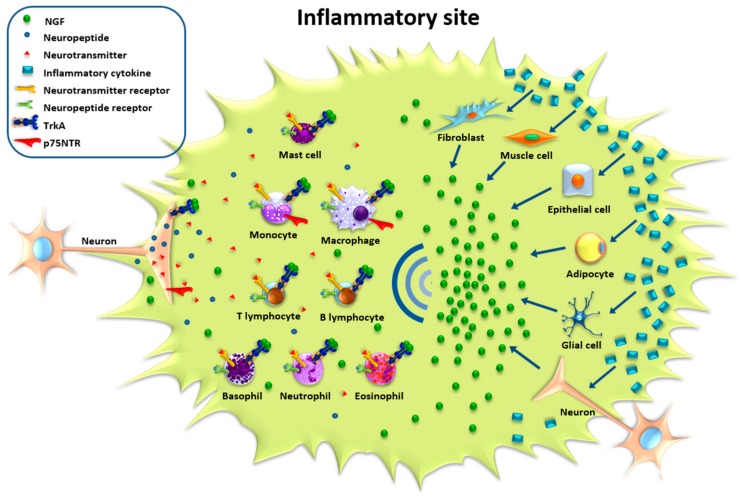
Figure 1.
Direct and indirect effects of nerve growth factor (NGF) on inflammatory responses. At the site of inflammation, inflammatory cytokines induce (blue arrows) the production of NGF in different cell types, such as muscle cells, epithelial cells, fibroblasts, adipocytes, neurons, glia, and immune cells. The enhanced local production of NGF influences nerve fiber distribution and neuronal activity, inducing the synthesis and release of neuropeptides and neurotransmitters that have immunomodulatory effects. NGF receptors are also expressed on the membrane of immune cells and NGF can directly modulate the activity and functions of immune cells.