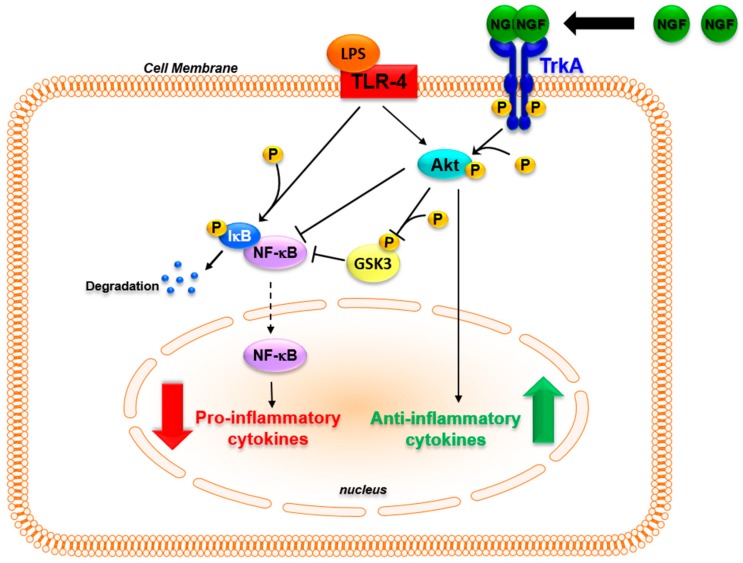
Figure 2.
TrkA activation promotes anti-inflammatory pathways. In human monocytes the expression of TrkA is enhanced when TLR4 is activated. Auto-phosphorylation of TrkA induced by NGF binding activates intracellular pathways that influence the downstream signaling of TLR4. The NGF-induced phosphorylation of Akt inhibits NF-κB translocation in the nucleus. The inhibitory phosphorylation of GSK3 induced by Akt further prevents NF-κB activation, and the NF-κB-dependent transcription of pro-inflammatory cytokine genes. Concomitantly, NGF activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway induces the expression of IL-10 and IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra), promoting a net anti-inflammatory effect. Black bold arrow shows dimerization of NGF and binding to TrkA. Red and green bold arrows show respectively decrease and increase of cytokine levels. Black slim arrows and black T bar show respectively activation and inhibition of molecular pathways. Dotted line arrow show nuclear translocation.