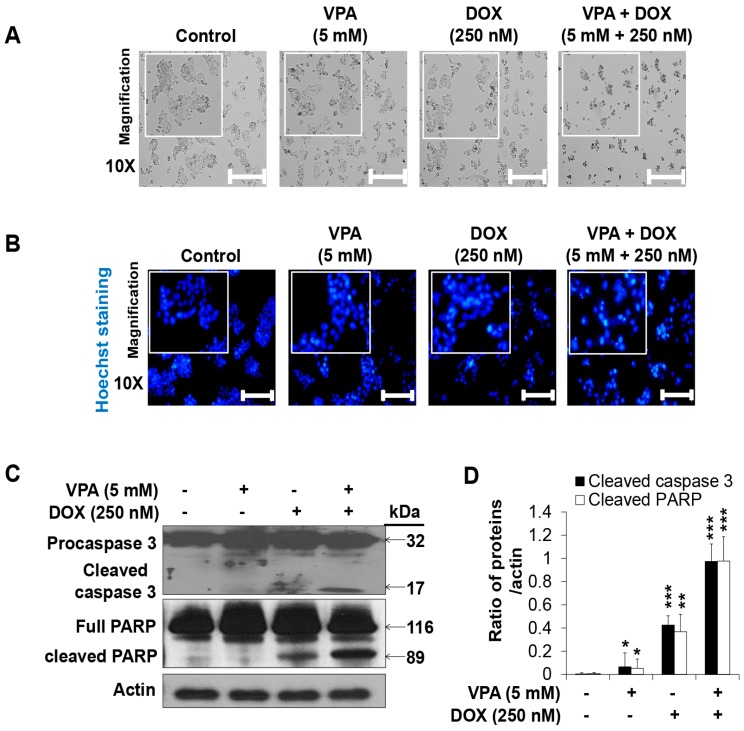
Figure 2.
The combination treatment of valproic acid (VPA) and doxorubicin (DOX) synergistically induced apoptosis of HepG2 cells. (A) Morphology of HepG2 cells treated with monotherapies and combination treatment of VPA and DOX at indicated concentration after 48-h treatment. Images were taken using phase contrast inverted light microscopy. Scale bar represents 200 μm; (B) Hoechst nuclear staining was used to detect apoptosis with condensed and fragmented nucleus in HepG2 cells after 48-h incubation with the indicated concentration of VPA and DOX monotherapies and the combination treatment. Images were taken using fluorescence inverted microscopy. Scale bar represents 200 μm; (C) Levels of pro- and cleaved-caspase3 and full length-and cleaved-PARP were analyzed in the indicated treated cells by using Western blotting. Actin was used as the loading control; (D) The intensity of cleaved-caspase3 and cleaved-PARP bands were quantified by scanning densitometry program ImageJ and normalized to that of actin. At least three independent experiments were performed and results shown as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 compared with the control group.