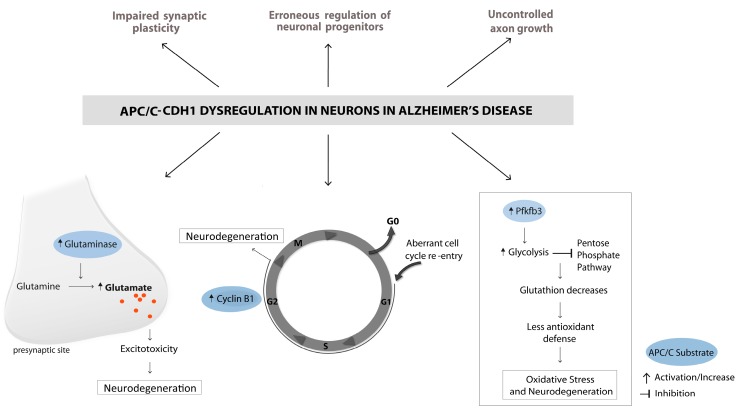
Figure 4.
Dysregulation of APC/C-Cdh1 in Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) may affect several different functions in neurons. Pathways involving APC/C substrates that cause excitotoxicity, cell cycle re-entry, and oxidative stress have been related to neurodegeneration. Furthermore, APC/C inactivation in AD could potentially lead to dysregulation of synaptic plasticity, neurogenesis, and axon growth.