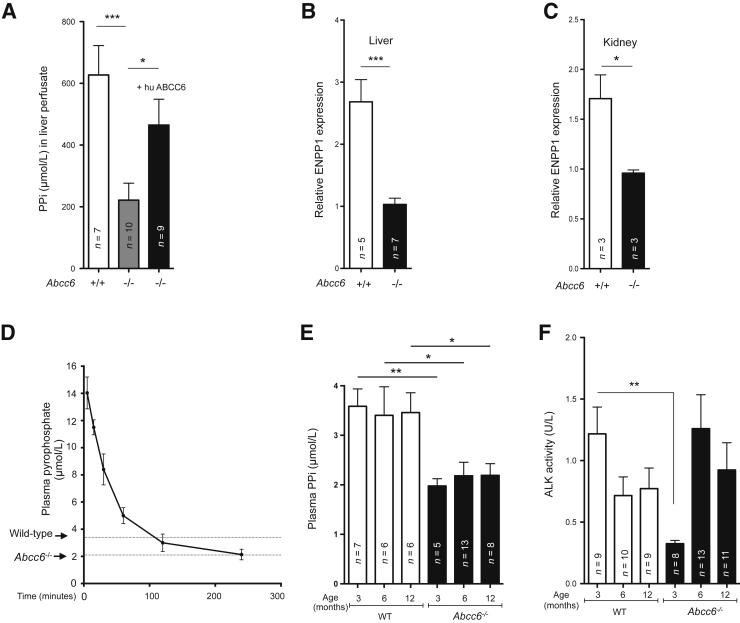
Figure 1.
Pyrophosphate (PPi) and bisphosphonates. A: The generation of ABCC6-dependent hepatic PPi was estimated in liver perfusate. The concentration of PPi in the perfusate buffer was compared between wild-type (WT; +/+) and Abcc6−/− mice (−/−), and to Abcc6−/− mice transiently expressing the human ABCC6 in liver. The relative level of expression of ENPP1 in the liver (B) and kidneys (C) of Abcc6−/− mice and wild-type mice was determined by real-time PCR using specific TaqMan probes. The data were normalized to the mouse GAPDH. D: PPi plasma concentration steadily decreases after a single i.p. injection of PPi at 112 μmol/kg (50 mg/kg) in Abcc6−/− mice with an approximate half-life of 42 minutes. Average plasma PPi levels of wild-type and Abcc6−/− mice are indicated. E: Plasma PPi concentration was significantly reduced in Abcc6−/− mice at 3-, 6-, and 12-month-old mice. At each time point, PPi levels were significantly lower in Abcc6−/− mice, though age does not influence PPi levels in either wild-type (+/+) or Abcc6−/− mice (−/−). F: Alkaline phosphatase activity (ALK) expressed as units (μmol of p-nitrophenyl/L per minute) was measured in plasma samples from the same 3-, 6-, and 12-month-old wild-type (+/+) and Abcc6−/− mice (−/−) as shown in E. The number of mice per group is shown. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 3 per data point (D). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001.