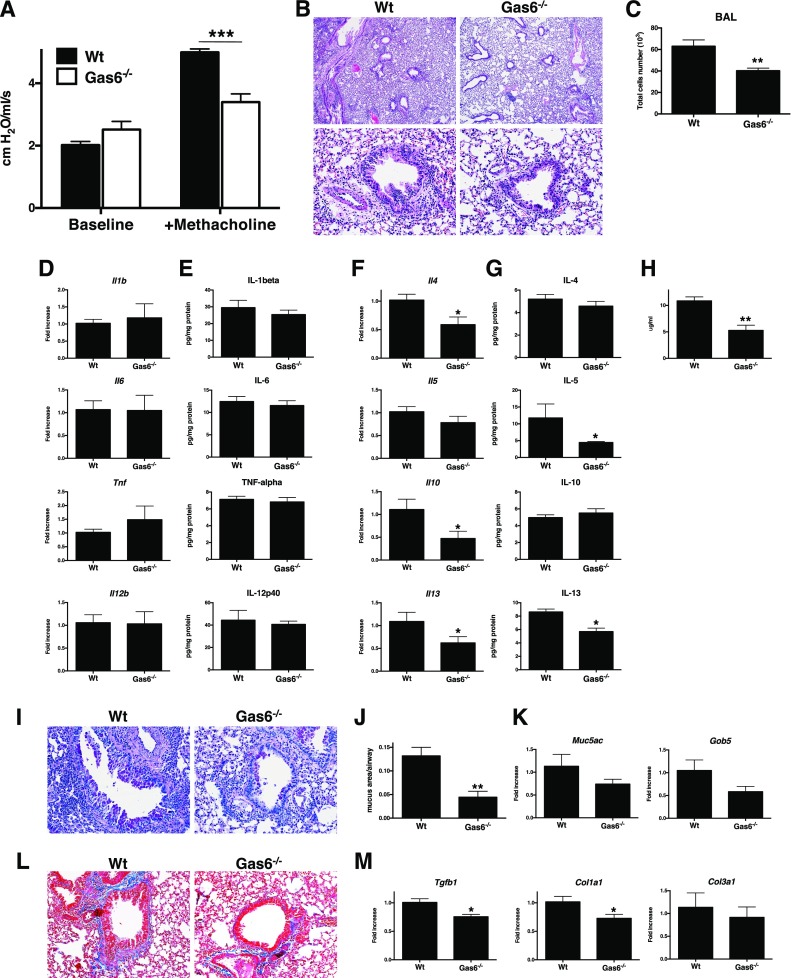
Figure 2.
Endogenous Gas6 facilitates methacholine-induced bronchoconstriction in allergic airway disease. (A) Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) to a methacholine challenge (420 μg/kg) was determined in Aspergillus fumigatus–sensitized wild-type (Wt) mice or Gas6-deficient (Gas6−/−) mice at Day 28 after conidia challenge. (B) Representative hematoxylin and eosin–stained lung tissue sections from Wt and Gas6−/− mice at Day 28 after conidia challenge. Original magnification: ×40 (upper) and ×200 (lower). (C) Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cell counts from both groups of mice. (D and E) Transcript (D) and protein (E) levels of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-12p40, and TNF-α in Wt and Gas6−/− mice at Day 28 after conidia challenge. (F and G) Whole lung transcript (F) and protein (G) levels of IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, and IL-13 in Wt and Gas6−/− mice at Day 28 after conidia challenge. (H) Serum IgE levels in Wt and Gas6−/− mice at Day 28 after conidia challenge. (I) Representative Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)-stained lung tissue sections from Wt and Gas6−/− mice at Day 28 after conidia challenge. (J) Quantitative pathological analysis of mucus area in G. (K) Quantitative PCR analysis of Muc5ac and Gob5 in Wt and Gas6−/− mice at Day 28 after conidia challenge. (L) Representative Masson trichrome–stained lung tissue sections from Wt and Gas6−/− mice at Day 28 after conidia challenge. (M) TGF-β, Col1a1, and Col3a1 transcript levels in Wt and Gas6−/− mice at Day 28 after conidia challenge. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM for n = 5 per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 versus Wt.