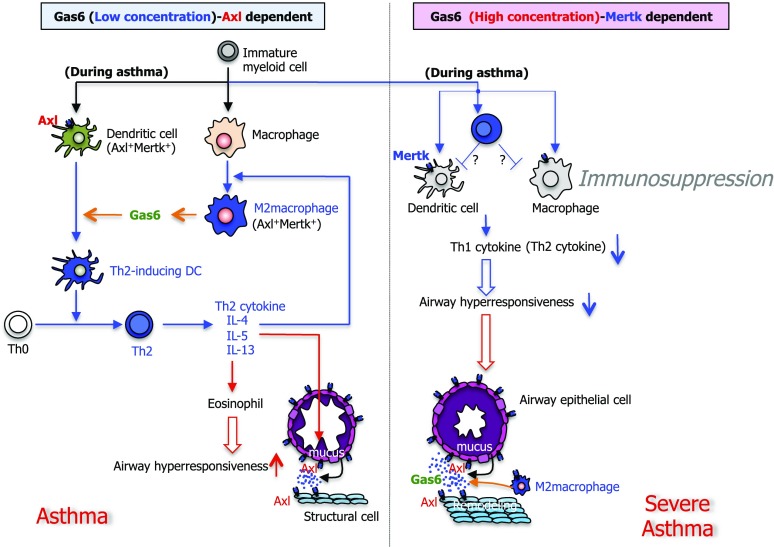
Figure 7.
Summary scheme outlining the manner in which Gas6 dose-dependently regulates lung immune and remodeling responses during primary allergic airway disease. In a dose-dependent manner, Gas6 modulated Th2-type inflammation, AHR, and airway and blood vessel remodeling during fungal allergic airway disease. Its mechanism of action appears to involve the generation of Gas6 by M2 macrophages leading to DC activation via Axl, which in turn polarized Th2 cells (left). However, Gas6 also exhibited immunoregulatory effects via Mertk activation in DCs and presumably other myeloid cell populations (right). Regardless of the lung levels of Gas6, it was apparent that this mediator exerted prominent airway remodeling characterized by goblet cell metaplasia and peribronchial fibrosis.