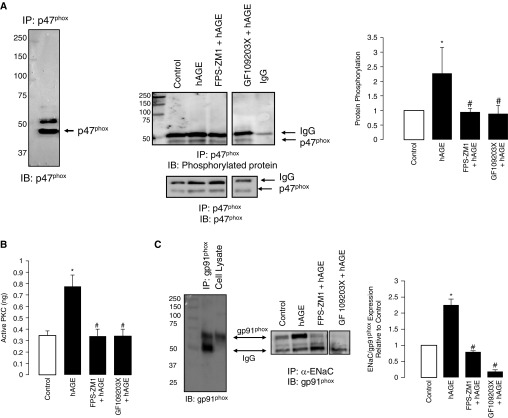
Figure 7.
Challenge with hAGEs increased phosphorylation of p47phox in isolated primary alveolar type 2 cells. (A) Western blot of immunoprecipitated p47phox protein that was immunoblotted for p47phox, showing molecular weight of approximately 47 kD; the slightly larger molecular weight band is IgG. Representative Western blot of immunoprecipitated p47phox protein immunoblotted for phosphorylated protein and normalized to total protein (lower panel) under control, hAGE, FPS-ZM1 plus hAGE, and GF109203X plus hAGE treatment conditions. Quantification of blot shows that hAGE treatment significantly increased 47phox phosphorylation, whereas treatment with FPS-ZM1 and GF109203X attenuated the effects of hAGE. (B) Active PKC of isolated primary type 2 cells was determined under control, hAGE, FPS-ZM1 plus hAGE, and GF109203X plus hAGE treatment. hAGE treatment significantly increased PKC activity, an effect that was abrogated with RAGE and PKC inhibition. (C) The left panel is an immunocontrol of immunoprecipitated gp91phox and cell lysate (both from alveolar type 2 cells) immunoblotted for gp91phox. The right panel is immunoprecipitated α-ENaC protein that was then immunoblotted for gp91phox (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate [NADPH] oxidases [Nox] 2) under control, hAGE, FPS-ZM1 plus hAGE, and GF109203X plus hAGE treatment conditions. Bar graph of Western blots showing that hAGEs increased coimmunoprecipitation of ENaC-Nox2, an effect that was attenuated when treated with either FPS-ZM1 or GF109203X. *P < 0.05 compared with control, #P < 0.05 compared with hAGEs.