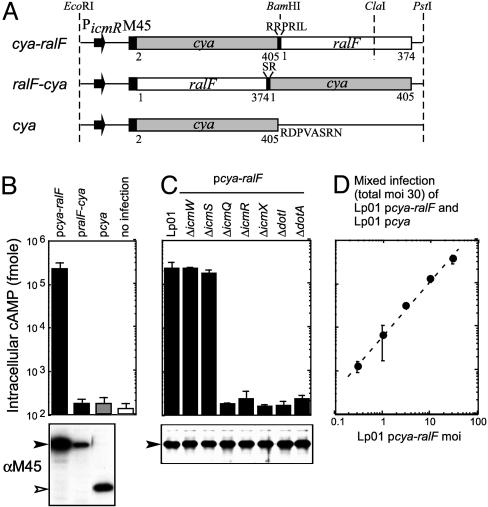
Fig. 1.
Quantitative analysis of RalF translocation into host cells. (A) Schematic representation of the Cya fusion constructs used to measure RalF translocation. Cya with RalF appended C-terminally (cya-ralF) and N-terminally (ralF-cya) are shown, as is the construct used as a negative control that produces only Cya (cya). The promoter and the translation initiation region of the Legionella icmR gene initiates transcription and translation of the fusion in each construct. All constructs have an N-terminal M45 epitope for immunological detection of the gene products. Regions derived from the Cya toxin of the Bordetella cya gene and the Legionella ralF gene are designated with amino acid residue numbers. Additional amino acid residues located at the fusion junctions and at the end of the Cya protein that resulted from the cloning procedures used are also indicated. These genes were ligated into pMMB207 and the resulting plasmids were designated as pcya-ralF,pralF-cya, and pcya, respectively. (B) CHO FcγRII cells were infected with wild-type Legionella harboring the indicated plasmids The y axis has cAMP levels detected for host cells infected for 1 h plotted on a logarithmic scale. Results are the average ± SD from an experiment performed in triplicate. Immunoblots shown below correspond to Cya protein levels inside of the Legionella cells used for the infection. (C) Requirements for Dot and Icm components in Cya-RalF translocation were examined. Isogenic Legionella mutants defective in the gene indicated at the top were derived from the wild-type strain Lp01. Immunoblots shown below correspond to Cya protein levels inside of the Legionella cells used for the infection. (D) The dynamic range of the Cya translocation assay was examined by adding Legionella at a multiplicity of infection (moi) of 30 to CHO FcγRII cells. The inoculum used was comprised of Legionella producing either Cya-RalF (pcya-ralF) or Cya alone (pcya) combined at different ratios. Plotted on the x axis is the number (moi) of Legionella producing Cya-RalF. The linear relationship between cAMP levels and the amount of Cya-RalF producing bacteria added indicate a dynamic range for this assay of at least 2 orders of magnitude.