Fig. 2.
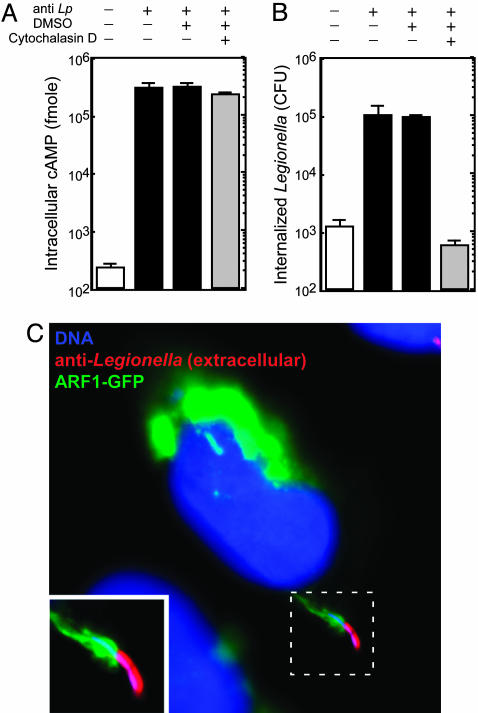
The RalF protein is translocated into host cells by extracellular Legionella. (A) CHO FcγRII cells were infected with Legionella producing Cya-RalF. Indicated above the graph is the addition (+) of opsonizing Ab (anti-Lp), DMSO, or Cytochalasin D dissolved in DMSO. Cya-RalF translocation levels were determined by measuring cAMP levels in host cells 1 h after infection. All values are the average ± SD for an experiment performed in triplicate. (B) In a parallel assay to that shown in A, CHO FcγRII cells were infected with Legionella producing Cya-RalF for 15 min and gentamicin was then added to kill extracellular bacteria. Internalized Legionella were determined 1 h after infection by plating bacteria that survived the gentamicin treatment on agar plates and counting colony-forming units. All values are the average ± SD for an experiment performed in triplicate. (C) CHO FcγRII cells producing ARF1-GFP (green) were infected for 5 min with opsonized Legionella (Lp01). Before permeabilization of the host cell plasma membrane, extracellular Legionella were stained with an anti-Legionella Ab (red). Host and bacterial DNA was stained with DAPI (blue) after permeabilization. This fluorescent micrograph shows an extracellular Legionella bacterium recruiting ARF1-GFP to the site of internalization.