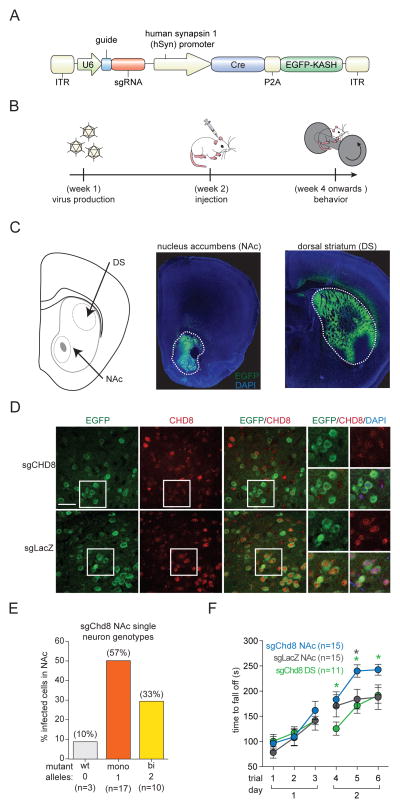
Figure 7. In vivo perturbation of Chd8 in adult mice recapitulates increased acquired motor learning phenotype.
(A) Diagram of AAV vector for sgRNA expression, Cas9 induction, and nuclei labeling in neurons of the Cre-dependent Cas9 mice.
(B) Workflow for generating and characterizing somatically edited Cre-dependent Cas9 mice.
(C) (Left) Schematic representation of a brain slice with the nucleus accumbens (NAc) and dorsal striatum (DS) target regions indicated. (Right) Representative immunofluorescence images four weeks post-injection showing AAV infected, EGFP-expressing neurons within the NAc and DS. Enclosed regions outline the targeted region. Also see Figure S7.
(D) Representative immunofluorescence images of AAV injected nucleus accumbens. Scale bar represents 50 μm.
(E) Indel analysis on Illumina sequencing reads from FACS sorted neuronal nuclei showing single cells with zero (wild-type, 10%), one (monoallelic, 57%), or two (biallelic, 33%) mutant alleles.
(F) In the rotarod performance test, sgChd8-NAc AAV injected mice (n = 15) spent more time on the rotating rod before falling off compared to sgChd8-DS (n = 11) and sgLacZ-NAc (n = 15) AAV injected control animals [sgChd8-NAc versus sgLacZ-NAc: repeated-measures two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test, adjusted p-value = 0.840 (Trial 1) > 0.05 (Trial 2) 0.732 (Trial 3) > 0.05 (Trial 4) > 0.026 (Trial 5) 0.031 (Trial 6); sgChd8-DS versus sgLacZ-DS: repeated-measures two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test, adjusted p-value > 0.05 (Trial 1) > 0.05 (Trial 2) > 0.05 (Trial 3) > 0.05 (Trial 4) > 0.05 (Trial 5) > 0.05 (Trial 6); sgChd8-NAc versus sgChd8-DS: repeated-measures two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test, adjusted p-value > 0.05 (Trial 1) > 0.05 (Trial 2) 0.815 (Trial 3) 0.036 (Trial 4) 0.011 (Trial 5) 0.074 (Trial 6)]. Also see Figure S7.