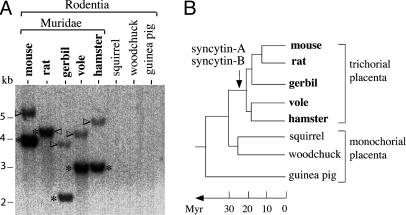
Fig. 7.
Conservation of the syncytin-A and -B genes during rodent evolution. (A) Southern blot of DraI-restricted genomic DNA from the indicated rodent species, with the syncytin-B fragments (asterisk) and the syncytin-A fragments (arrowhead) both found in Muridae only (the syncytin-A bands have a lower intensity due to the use of a syncytin-B probe, with the opposite result when using a syncytin-A probe; not shown). (B) Schematized rodent phylogenetic tree, with the arrow indicating the date of entry of the two syncytin-A and -B envelope genes; the placenta type, in terms of structure of the syncytiotrophoblast materno–fetal barrier, is indicated (see Discussion).